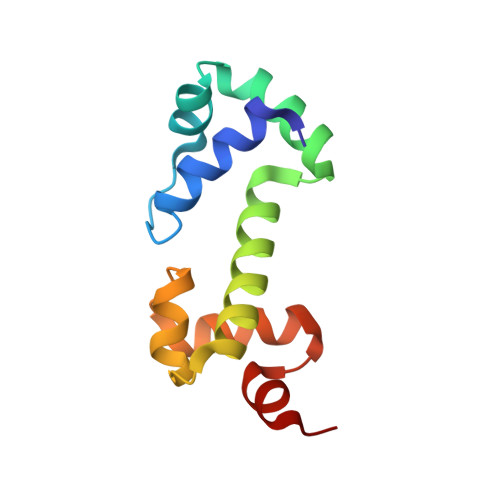
Solution structure of the DNA binding domain of AraC protein.
Rodgers, M.E., Schleif, R.(2009) Proteins 77: 202-208
- PubMed: 19422057
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22431
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2K9S - PubMed Abstract:
We report the solution structure of the DNA binding domain of the Escherichia coli regulatory protein AraC determined in the absence of DNA. The 20 lowest energy structures, determined on the basis of 1507 unambiguous nuclear Overhauser restraints and 180 angle restraints, are well resolved with a pair wise backbone root mean square deviation of 0.7 A. The protein, free of DNA, is well folded in solution and contains seven helices arranged in two semi-independent sub domains, each containing one helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif, joined by a 19 residue central helix. This solution structure is discussed in the context of extensive biochemical and physiological data on AraC and with respect to the DNA-bound structures of the MarA and Rob homologs.
- Biology Department, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland 21218, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: