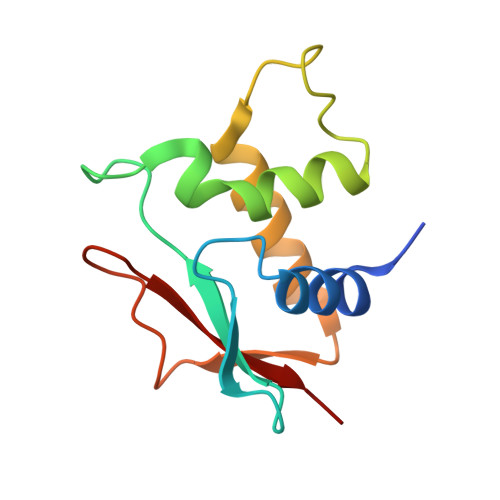
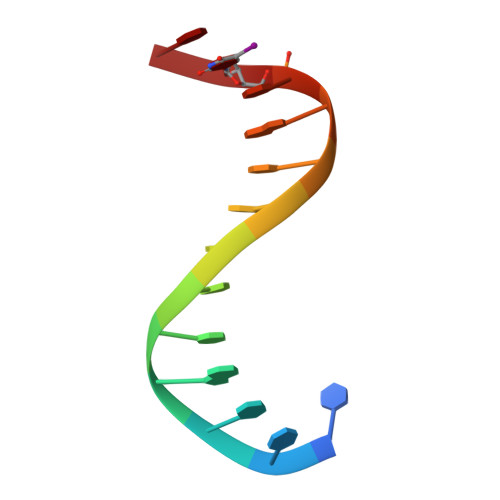
Crystal structure of an IRF-DNA complex reveals novel DNA recognition and cooperative binding to a tandem repeat of core sequences.
Fujii, Y., Shimizu, T., Kusumoto, M., Kyogoku, Y., Taniguchi, T., Hakoshima, T.(1999) EMBO J 18: 5028-5041
- PubMed: 10487755
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.18.5028
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2IRF - PubMed Abstract:
There has been growing interest in the role of the IRF (interferon regulatory factor) family of transcription factors in the regulation of immune responses, cytokine signaling, and oncogenesis. These members are characterized by their well-conserved DNA binding domains at the N-terminal regions. Here we report the 2.2 A resolution crystal structure of the DNA binding domain of one such family member, IRF-2, bound to DNA. The structure reveals its recognition sequence, AANNGAAA (here, recognized bases are underlined and in bold, and N indicates any base), and its cooperative binding to a tandem repeat of the GAAA core sequence induced by DNA structure distortions. These facts explain well the diverse binding properties of the IRF family members, which bind to both single and tandemly repeated sequences. Furthermore, we also identified the 'helix-hairpin-strand motif' at the C terminus of the recognition helix as a metal binding site that is commonly found in certain classes of DNA-interactive proteins. Our results provide new insights into the structure and function of this family of transcription factors.
- Department of Molecular Biology, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, 8916-5 Takayama, Ikoma, Nara 630-0101, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: