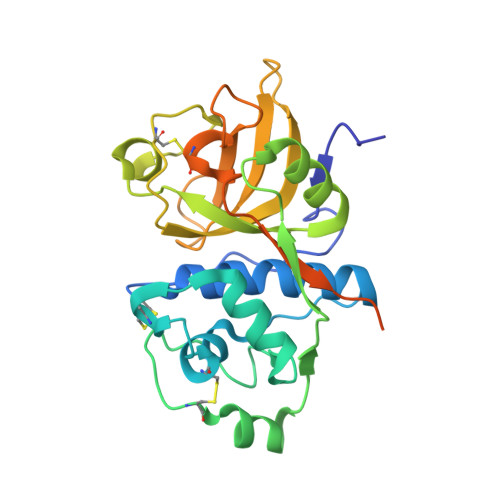
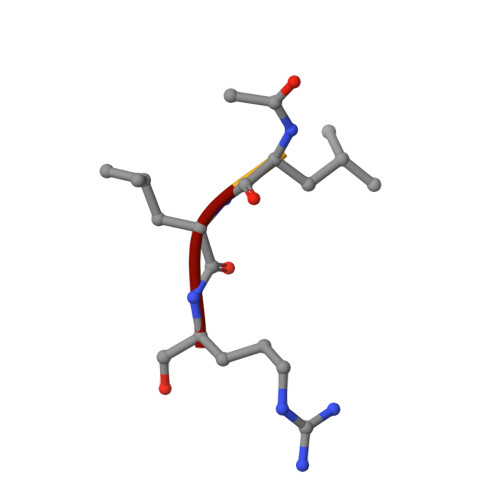
Heterologous Expression, Purification, Refolding, and Structural-Functional Characterization of EP-B2, a Self-Activating Barley Cysteine Endoprotease.
Bethune, M.T., Strop, P., Tang, Y., Sollid, L.M., Khosla, C.(2006) Chem Biol 13: 637-647
- PubMed: 16793521
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.04.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2FO5 - PubMed Abstract:
We describe the heterologous expression in Escherichia coli of the proenzyme precursor to EP-B2, a cysteine endoprotease from germinating barley seeds. High yields (50 mg/l) of recombinant proEP-B2 were obtained from E. coli inclusion bodies in shake flask cultures following purification and refolding. The zymogen was rapidly autoactivated to its mature form under acidic conditions at a rate independent of proEP-B2 concentration, suggesting a cis mechanism of autoactivation. Mature EP-B2 was stable and active over a wide pH range and efficiently hydrolyzed a recombinant wheat gluten protein, alpha2-gliadin, at sequences with known immunotoxicity in celiac sprue patients. The X-ray crystal structure of mature EP-B2 bound to leupeptin was solved to 2.2 A resolution and provided atomic insights into the observed subsite specificity of the endoprotease. Our findings suggest that orally administered proEP-B2 may be especially well suited for treatment of celiac sprue.
- Department of Biochemistry, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: