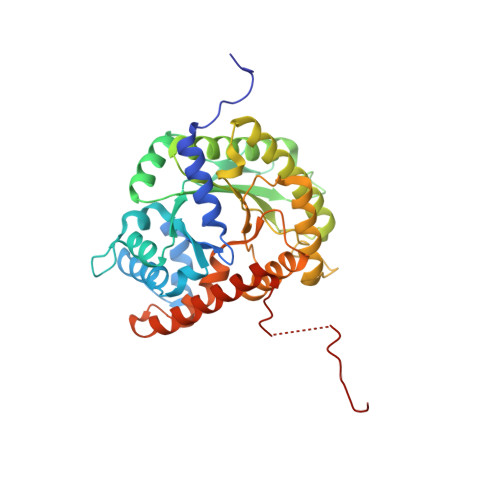
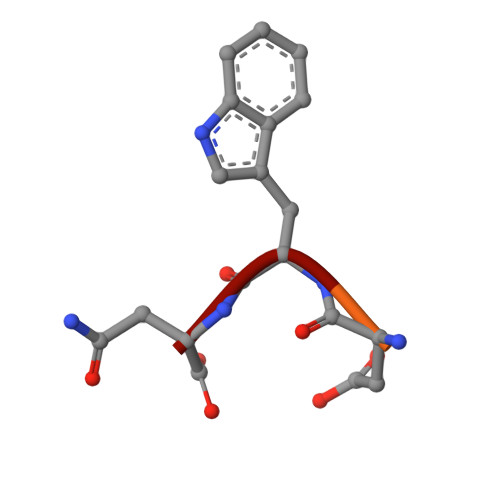
Aldolase provides an unusual binding site for thrombospondin-related anonymous protein in the invasion machinery of the malaria parasite.
Bosch, J., Buscaglia, C.A., Krumm, B., Ingason, B.P., Lucas, R., Roach, C., Cardozo, T., Nussenzweig, V., Hol, W.G.(2007) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 7015-7020
- PubMed: 17426153
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605301104
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2EPH, 2PC4 - PubMed Abstract:
An actomyosin motor located underneath the plasma membrane drives motility and host-cell invasion of apicomplexan parasites such as Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax, the causative agents of malaria. Aldolase connects the motor actin filaments to transmembrane adhesive proteins of the thrombospondin-related anonymous protein (TRAP) family and transduces the motor force across the parasite surface. The TRAP-aldolase interaction is a distinctive and critical trait of host hepatocyte invasion by Plasmodium sporozoites, with a likely similar interaction crucial for erythrocyte invasion by merozoites. Here, we describe 2.4-A and 2.7-A structures of P. falciparum aldolase (PfAldo) obtained from crystals grown in the presence of the C-terminal hexapeptide of TRAP from Plasmodium berghei. The indole ring of the critical penultimate Trp-residue of TRAP fits snugly into a newly formed hydrophobic pocket, which is exclusively delimited by hydrophilic residues: two arginines, one glutamate, and one glutamine. Comparison with the unliganded PfAldo structure shows that the two arginines adopt new side-chain rotamers, whereas a 25-residue subdomain, forming a helix-loop-helix unit, shifts upon binding the TRAP-tail. The structural data are in agreement with decreased TRAP binding after mutagenesis of PfAldo residues in and near the induced TRAP-binding pocket. Remarkably, the TRAP- and actin-binding sites of PfAldo seem to overlap, suggesting that both the plasticity of the aldolase active-site region and the multimeric nature of the enzyme are crucial for its intriguing nonenzymatic function in the invasion machinery of the malaria parasite.
- Department of Biochemistry and Structural Genomics of Pathogenic Protozoa (SGPP) Consortium, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: