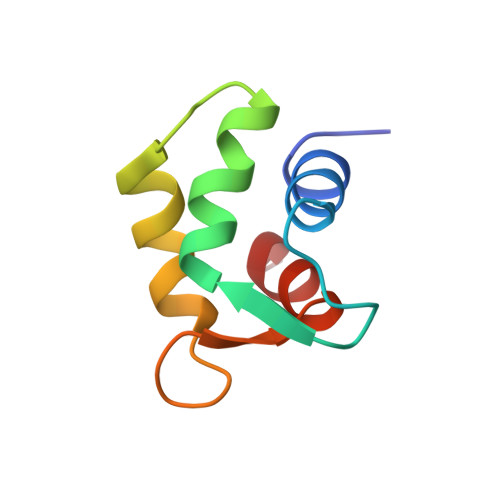
A Structural and Dynamic Characterization of the EF-Hand Protein CLSP.
Babini, E., Bertini, I., Capozzi, F., Chirivino, E., Luchinat, C.(2006) Structure 14: 1029-1038
- PubMed: 16765896
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2006.04.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2B1U - PubMed Abstract:
The structure and dynamics of human calmodulin-like skin protein (CLSP) have been characterized by NMR spectroscopy. The mobility of CLSP has been found to be different for the N-terminal and C-terminal domains. The isolated domains were also expressed and analyzed. The structure of the isolated C-terminal domain is presented. The N-terminal domain is characterized by four stable helices, which experience large fluctuations. This is shown to be due to mutations in the hydrophobic core. The overall N-terminal domain behavior is similar both in the full-length protein and in the isolated domain. By exploiting the capability of Tb3+ bound to CLSP to induce partial orientation of the molecule in a magnetic field, restricted motion of one domain with respect to the other was proved. By using NMR, ITC, and ESI-MS, the calcium and magnesium binding properties were investigated. Finally, CLSP is framed into the evolutionary scheme of the calmodulin-like family.
- Centro Risonanze Magnetiche, University of Florence, Via Sacconi 6, 50019 Sesto Fiorentino, Florence, Italy.
Organizational Affiliation: