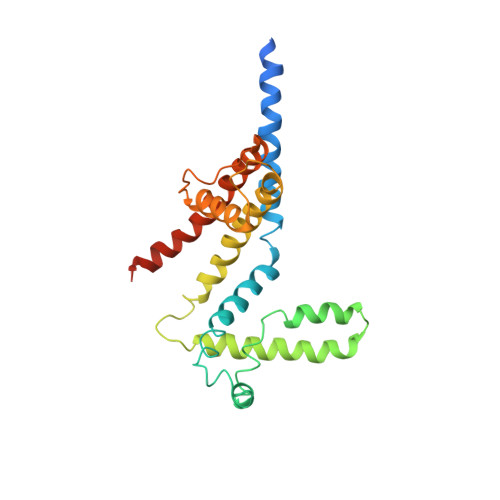
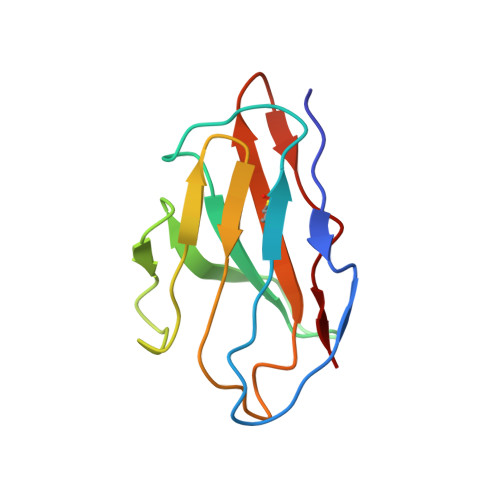
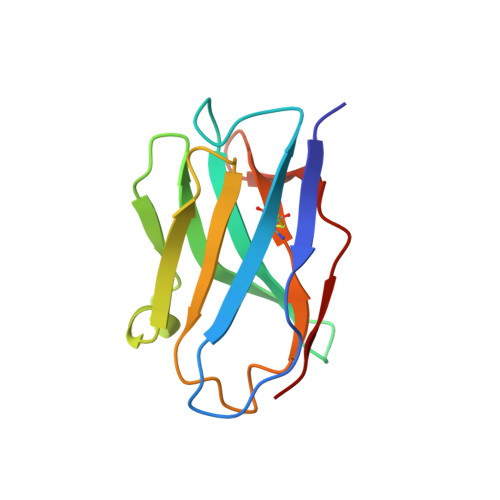
Structure of the KvAP voltage-dependent K+ channel and its dependence on the lipid membrane.
Lee, S.Y., Lee, A., Chen, J., Mackinnon, R.(2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 15441-15446
- PubMed: 16223877
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507651102
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2A0L - PubMed Abstract:
Voltage-dependent ion channels gate open in response to changes in cell membrane voltage. This form of gating permits the propagation of action potentials. We present two structures of the voltage-dependent K(+) channel KvAP, in complex with monoclonal Fv fragments (3.9 A) and without antibody fragments (8 A). We also studied KvAP with disulfide cross-bridges in lipid membranes. Analyzing these data in the context of the crystal structure of Kv1.2 and EPR data on KvAP we reach the following conclusions: (i) KvAP is similar in structure to Kv1.2 with a very modest difference in the orientation of its voltage sensor; (ii) mAb fragments are not the source of non-native conformations of KvAP in crystal structures; (iii) because KvAP contains separate loosely adherent domains, a lipid membrane is required to maintain their correct relative orientations, and (iv) the model of KvAP is consistent with the proposal of voltage sensing through the movement of an arginine-containing helix-turn-helix element at the protein-lipid interface.
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Laboratory of Molecular Neurobiology and Biophysics, The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Avenue, New York, NY 10021, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: