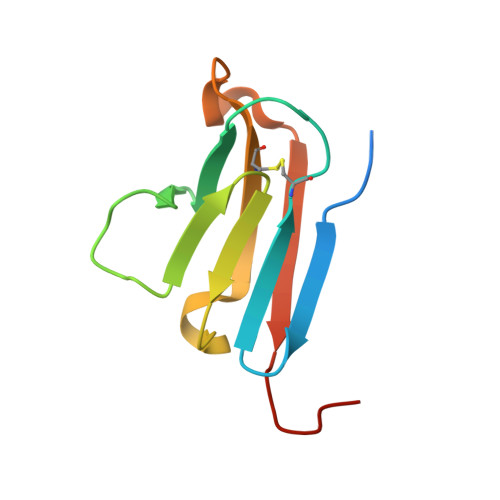
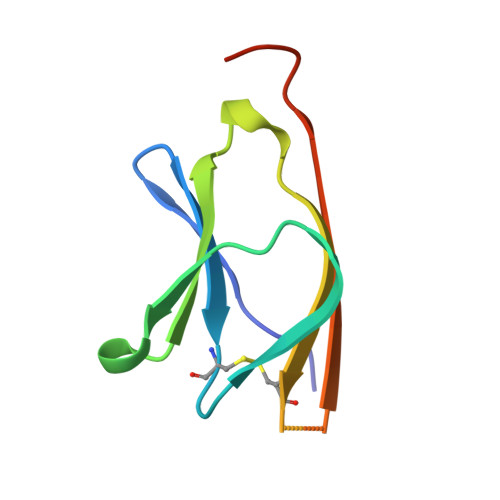
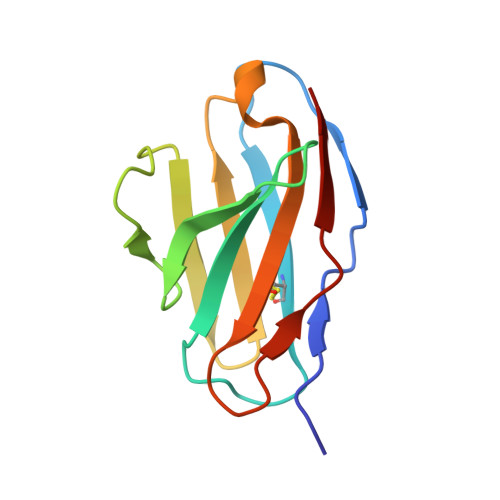
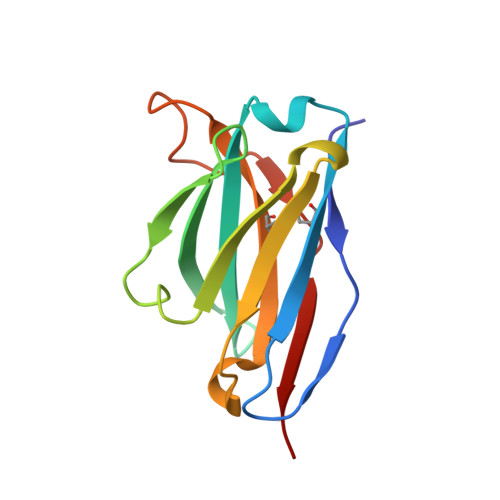
Crystal structure of a human CD3-epsilon/delta dimer in complex with a UCHT1 single-chain antibody fragment.
Arnett, K.L., Harrison, S.C., Wiley, D.C.(2004) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101: 16268-16273
- PubMed: 15534202
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407359101
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XIW - PubMed Abstract:
The alpha/beta T cell receptor complex transmits signals from MHC/peptide antigens through a set of constitutively associated signaling molecules, including CD3-epsilon/gamma and CD3-epsilon/delta. We report the crystal structure at 1.9-A resolution of a complex between a human CD3-epsilon/delta ectodomain heterodimer and a single-chain fragment of the UCHT1 antibody. CD3-epsilon/delta and CD3-epsilon/gamma share a conserved interface between the Ig-fold ectodomains, with parallel packing of the two G strands. CD3-delta has a more electronegative surface and a more compact Ig fold than CD3-gamma; thus, the two CD3 heterodimers have distinctly different molecular surfaces. The UCHT1 antibody binds near an acidic region of CD3-epsilon opposite the dimer interface, occluding this region from direct interaction with the TCR. This immunodominant epitope may be a uniquely accessible surface in the TCR/CD3 complex, because there is overlap between the binding site of the UCHT1 and OKT3 antibodies. Determination of the CD3-epsilon/delta structure completes the set of TCR/CD3 globular ectodomains and contributes information about exposed CD3 surfaces.
- Department of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard Medical School, 250 Longwood Avenue, Boston, MA 02115, USA. arnett@crystal.harvard.edu
Organizational Affiliation: