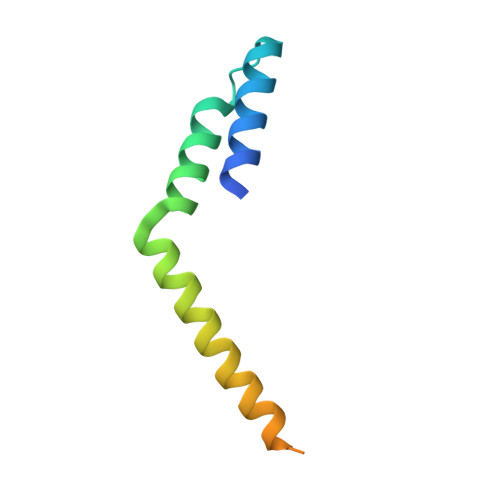
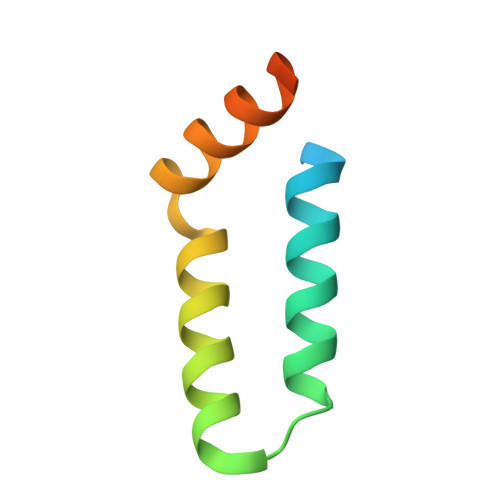
Structural basis for L27 domain-mediated assembly of signaling and cell polarity complexes.
Li, Y., Karnak, D., Demeler, B., Margolis, B., Lavie, A.(2004) EMBO J 23: 2723-2733
- PubMed: 15241471
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600294
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1VF6 - PubMed Abstract:
L27 is a protein-binding domain that can assemble essential proteins for signaling and cell polarity into complexes by interacting in a heterodimeric manner. One of these protein complexes is the PATJ/PALS1/Crumbs tripartite complex, which is crucial for the establishment and maintenance of cell polarity. To reveal the structural basis underlining the obligate heterodimerization, we have determined the crystal structure of the PALS1-L27N/PATJ-L27 heterodimer complex. Each L27 domain is composed of three helices. The two L27 domains heterodimerize by building a compact structure consisting of a four-helix bundle formed by the first two helices of each L27 domain and one coiled-coil formed by the third helix of each domain. The large hydrophobic packing interactions contributed by all the helices of both L27 domains predominantly drive the heterodimer formation, which is likely to be a general feature of L27 domains. Combined with mutational studies, we can begin to understand the structural basis for the specificity of L27 binding pairs. Our results provide unique insights into L27 domain heterodimer complex, which is critical for cell polarization.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, University of Illinois, Chicago, IL 60607, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: