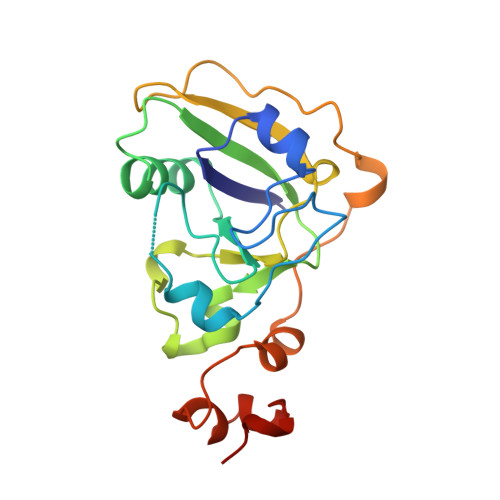
Crystal structure of a new heat-labile enterotoxin, LT-IIb.
van den Akker, F., Sarfaty, S., Twiddy, E.M., Connell, T.D., Holmes, R.K., Hol, W.G.(1996) Structure 4: 665-678
- PubMed: 8805549
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00073-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1TII - PubMed Abstract:
Cholera toxin from Vibrio cholerae and the type I heat-labile enterotoxins (LT-Is) from Escherichia coli are oligomeric proteins with AB5 structures. The type II heat-labile enterotoxins (LT-IIs) from E. coli are structurally similar to, but antigenically distinct from, the type I enterotoxins. The A subunits of type I and type II enterotoxins are homologous and activate adenylate cyclase by ADP-ribosylation of a G protein subunit, G8 alpha. However, the B subunits of type I and type II enterotoxins differ dramatically in amino acid sequence and ganglioside-binding specificity. The structure of LT-IIb was determined both as a prototype for other LT-IIs and to provide additional insights into structure/function relationships among members of the heat-labile enterotoxin family and the superfamily of ADP-ribosylating protein toxins. The 2.25 A crystal structure of the LT-IIb holotoxin has been determined. The structure reveals striking similarities with LT-I in both the catalytic A subunit and the ganglioside-binding B subunits. The latter form a pentamer which has a central pore with a diameter of 10-18 A. Despite their similarities, the relative orientation between the A polypeptide and the B pentamer differs by 24 degrees in LT-I and LT-IIb. A common hydrophobic ring was observed at the A-B5 interface which may be important in the cholera toxin family for assembly of the AB5 heterohexamer. A cluster of arginine residues at the surface of the A subunit of LT-I and cholera toxin, possibly involved in assembly, is also present in LT-IIb. The ganglioside receptor binding sites are localized, as suggested by mutagenesis, and are in a position roughly similar to the sites where LT-I binds its receptor. The structure of LT-IIb provides insight into the sequence diversity and structural similarity of the AB5 toxin family. New knowledge has been gained regarding the assembly of AB5 toxins and their active-site architecture.
- Department of Biological Structure and Biochemistry, University of Washington, Seattle 98195, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: