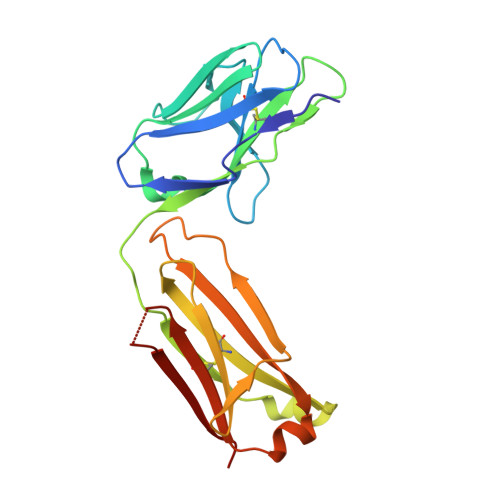
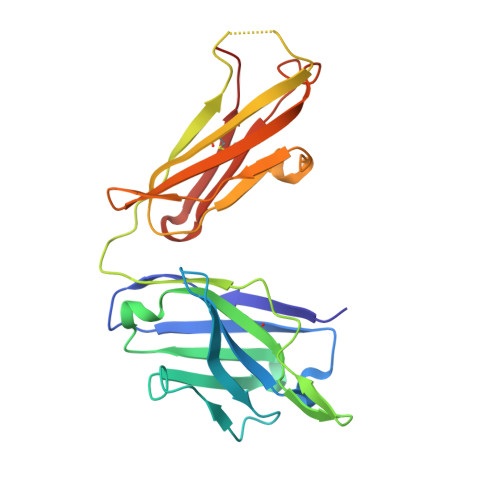
Neutralization of NGF-TrkA Receptor Interaction by the Novel Antagonistic anti-TrkA Monoclonal Antibody MNAC13: a Structural Insight
Covaceuszach, S., Cattaneo, A., Lamba, D.(2005) Proteins 58: 717-727
- PubMed: 15625712
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.20366
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SEQ - PubMed Abstract:
MNAC13, a mouse monoclonal antibody, recognizes with high affinity and specificity the neurotrophin receptor TrkA and displays a neutralizing activity toward the NGF/TrkA interaction. Detailed knowledge of the molecular basis determining the specificity of this antibody is of importance because of its potential use as a modulator of the TrkA-mediated NGF activity. Here, we report a full biochemical and structural characterization of the MNAC13 antibody. Epitope mapping studies, by serial deletion mutants and by phage display, reveal a conformational epitope that is localized on the carboxy-terminal region of the first immunoglobulin-like domain (d4) of TrkA. The X-ray crystal structure of the MNAC13 Fab fragment has been determined and refined to 1.8 A resolution. The antigen-binding site is characterized by a crevice, surrounded by hydrophilic-charged residues on either side, dipping deep toward three mainly hydrophobic subsites. Remarkably an isopropanol molecule has been found to bind in one of the hydrophobic crevices. Overall, the surface topology (shape and electrostatic potential) of the combining site is consistent with the binding data on TrkA ECD serial deletions mutants. The structure of the MNAC13 Fab fragment may assist in the rational structure-based design of high affinity humanized forms of MNAC13, appropriate for therapeutic approaches in neuropathy and inflammatory pain states.
- LaylineGenomics, Roma, Italy. covaceu@sissa.it <covaceu@sissa.it>
Organizational Affiliation: