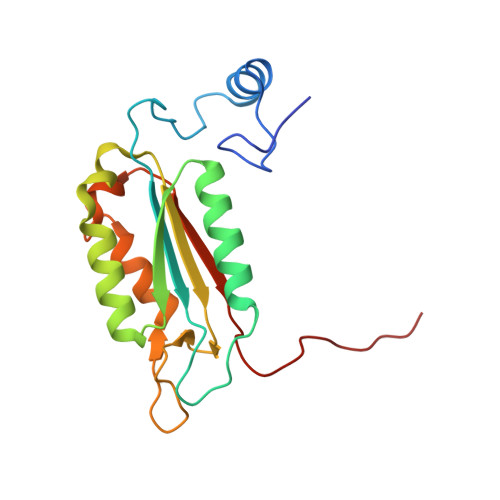
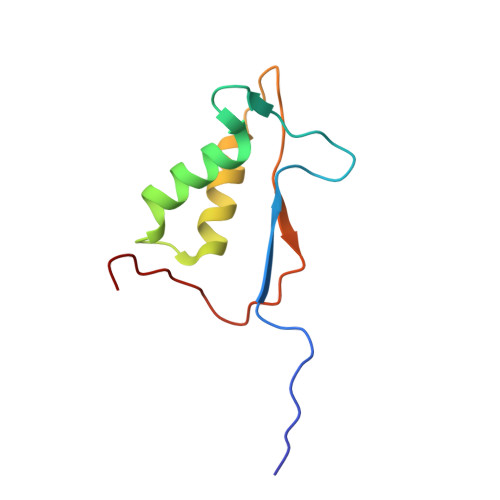
Tethering identifies fragment that yields potent inhibitors of human caspase-1.
Fahr, B.T., O'Brien, T., Pham, P., Waal, N.D., Baskaran, S., Raimundo, B.C., Lam, J.W., Sopko, M.M., Purkey, H.E., Romanowski, M.J.(2006) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 559-562
- PubMed: 16274992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.10.048
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RWW, 1RWX - PubMed Abstract:
Disulfide Tethering was applied to the active site of human caspase-1, resulting in the discovery of a novel, tricyclic molecular fragment that selectively binds in S4. This fragment was developed into a class of potent inhibitors of human caspase-1. Several key analogues determined the optimal distance of the tricycle from the catalytic residues, the relative importance of various features of the tricycle, and the importance of the linker.
- Department of Chemistry, Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, 341 Oyster Point Boulevard, South San Francisco, CA 94080, USA. bfahr@sunesis.com
Organizational Affiliation: