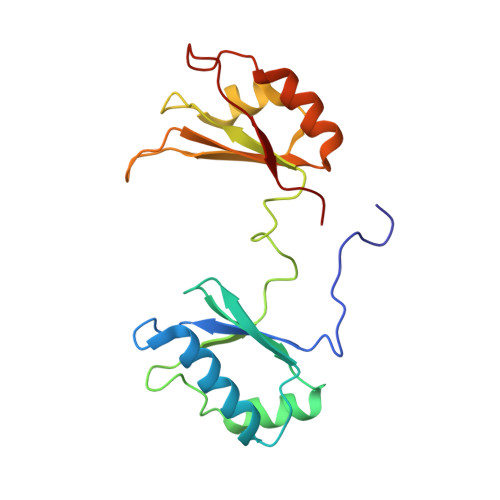
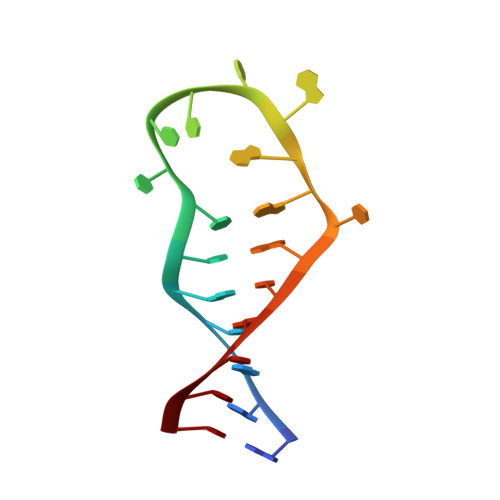
Solution structure of the complex formed by the two N-terminal RNA-binding domains of nucleolin and a pre-rRNA target.
Johansson, C., Finger, L.D., Trantirek, L., Mueller, T.D., Kim, S., Laird-Offringa, I.A., Feigon, J.(2004) J Mol Biology 337: 799-816
- PubMed: 15033352
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.01.056
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RKJ - PubMed Abstract:
Nucleolin is a 70 kDa multidomain protein involved in several steps of eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis. In vitro selection in combination with mutagenesis and structural analysis identified binding sites in pre-rRNA with the consensus (U/G)CCCG(A/G) in the context of a hairpin structure, the nucleolin recognition element (NRE). The central region of the protein contains four tandem RNA-binding domains (RBDs), of which the first two are responsible for the RNA-binding specificity and affinity for NREs. Here, we present the solution structure of the 28 kDa complex formed by the two N-terminal RNA-binding domains of nucleolin (RBD12) and a natural pre-rRNA target, b2NRE. The structure demonstrates that the sequence-specific recognition of the pre-rRNA NRE is achieved by intermolecular hydrogen bonds and stacking interactions involving mainly the beta-sheet surfaces of the two RBDs and the linker residues. A comparison with our previously determined NMR structure of RBD12 in complex with an in vitro selected RNA target, sNRE, shows that although the sequence-specific recognition of the loop consensus nucleotides is the same in the two complexes, they differ in several aspects. While the protein makes numerous specific contacts to the non-consensus nucleotides in the loop E motif (S-turn) in the upper part of the sNRE stem, nucleolin RBD12 contacts only consensus nucleotides in b2NRE. The absence of these upper stem contacts from the RBD12/b2NRE complex results in a much less stable complex, as demonstrated by kinetic analyses. The role of the loop E motif in high-affinity binding is supported by gel-shift analyses with a series of sNRE mutants. The less stable interaction of RBD12 with the natural RNA target is consistent with the proposed role of nucleolin as a chaperone that interacts transiently with pre-rRNA to prevent misfolding.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Molecular Biology Institute, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095-1569, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: