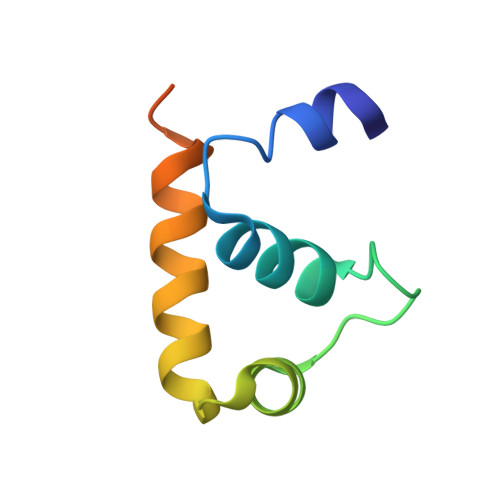
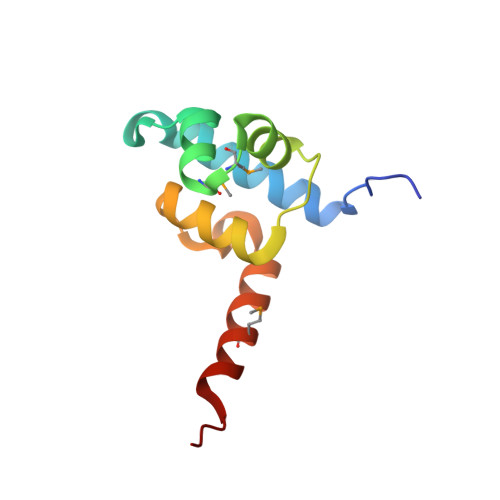
Structure of a ternary transcription activation complex.
Jain, D., Nickels, B.E., Sun, L., Hochschild, A., Darst, S.A.(2004) Mol Cell 13: 45-53
- PubMed: 14731393
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00483-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RIO - PubMed Abstract:
The cI protein of bacteriophage lambda (lambdacI) activates transcription by binding a DNA operator just upstream of the promoter and interacting with the RNA polymerase sigma subunit domain 4 (sigma(4)). We determined the crystal structure of the lambdacI/sigma(4)/DNA ternary complex at 2.3 A resolution. There are no conformational changes in either protein, which interact through an extremely small interface involving at most 6 amino acid residues. The interactions of the two proteins stabilize the binding of each protein to the DNA. The results provide insight into how activators can operate through a simple cooperative binding mechanism but affect different steps of the transcription initiation process.
- The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Avenue, New York, NY 10021, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: