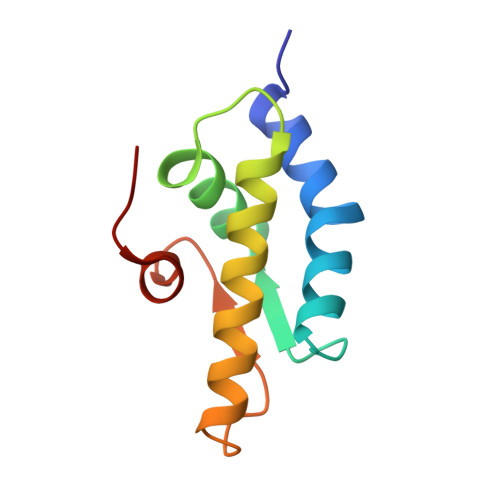
Crystal structure of the AAA+ alpha domain of E. coli Lon protease at 1.9A resolution.
Botos, I., Melnikov, E.E., Cherry, S., Khalatova, A.G., Rasulova, F.S., Tropea, J.E., Maurizi, M.R., Rotanova, T.V., Gustchina, A., Wlodawer, A.(null) J Struct Biol 146: 113-122
- PubMed: 15037242
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2003.09.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QZM - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of the small, mostly helical alpha domain of the AAA+ module of the Escherichia coli ATP-dependent protease Lon has been solved by single isomorphous replacement combined with anomalous scattering and refined at 1.9A resolution to a crystallographic R factor of 17.9%. This domain, comprising residues 491-584, was obtained by chymotrypsin digestion of the recombinant full-length protease. The alpha domain of Lon contains four alpha helices and two parallel strands and resembles similar domains found in a variety of ATPases and helicases, including the oligomeric proteases HslVU and ClpAP. The highly conserved "sensor-2" Arg residue is located at the beginning of the third helix. Detailed comparison with the structures of 11 similar domains established the putative location of the nucleotide-binding site in this first fragment of Lon for which a crystal structure has become available.
- Macromolecular Crystallography Laboratory, National Cancer Institute at Frederick, MCL Bldg. 536, Rm. 5, Frederick, MD 21702-1201, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: