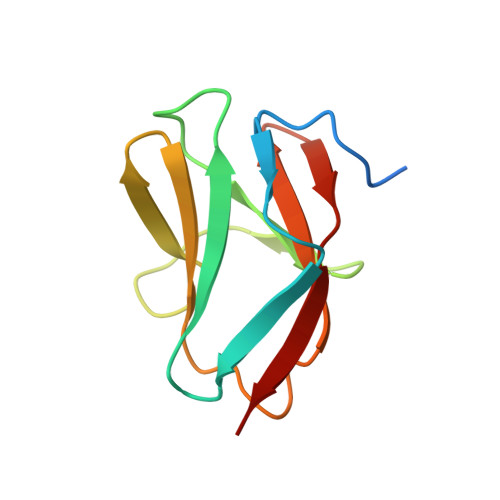
Dissecting the N-terminal myosin binding site of human cardiac myosin-binding protein C. Structure and myosin binding of domain C2
Ababou, A., Gautel, M., Pfuhl, M.(2007) J Biological Chem 282: 9204-9215
- PubMed: 17192269
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M610899200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PD6 - PubMed Abstract:
Myosin-binding protein C (MyBP-C) binds to myosin with two binding sites, one close to the N terminus and the other at the C terminus. Here we present the solution structure of one part of the N-terminal binding site, the third immunoglobulin domain of the cardiac isoform of human MyBP-C (cC2) together with a model of its interaction with myosin. Domain cC2 has the beta-sandwich structure expected from a member of the immunoglobulin fold. The C-terminal part of the structure of cC2 is very closely related to telokin, the myosin binding fragment of myosin light chain kinase. Domain cC2 also contains two cysteines on neighboring strands F and G, which would be able to form a disulfide bridge in a similar position as in telokin. Using NMR spectroscopy and isothermal titration calorimetry we demonstrate that cC2 alone binds to a fragment of myosin, S2Delta, with low affinity (kD = 1.1 mM) but exhibits a highly specific binding site. This consists of the C-terminal surface of the C'CFGA' beta-sheet, which includes Glu(301), a residue mutated to Gln in the disease familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The binding site on S2 was identified by a combination of NMR binding experiments of cC2 with S2Delta containing the cardiomyopathy-linked mutation R870H and molecular modeling. This mutation lowers the binding affinity and changes the arrangement of side chains at the interface. Our model of the cC2-S2Delta complex gives a first glimpse of details of the MyBP-C-myosin interaction. Using this model we suggest that most key interactions are between polar amino acids, explaining why the mutations E301Q in cC2 and R870H in S2Delta could be involved in cardiomyopathy. We expect that this model will stimulate future research to further refine the details of this interaction and their importance for cardiomyopathy.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Leicester, University Road, Leicester LE1 7RH.
Organizational Affiliation: