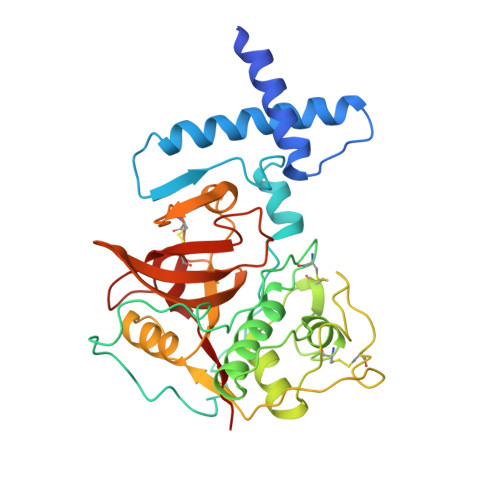
The prosequence of procaricain forms an alpha-helical domain that prevents access to the substrate-binding cleft.
Groves, M.R., Taylor, M.A., Scott, M., Cummings, N.J., Pickersgill, R.W., Jenkins, J.A.(1996) Structure 4: 1193-1203
- PubMed: 8939744
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00127-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PCI - PubMed Abstract:
Cysteine proteases are involved in a variety of cellular processes including cartilage degradation in arthritis, the progression of Alzheimer's disease and cancer invasion: these enzymes are therefore of immense biological importance. Caricain is the most basic of the cysteine proteases found in the latex of Carica papaya. It is a member of the papain superfamily and is homologous to other plant and animal cysteine proteases. Caricain is naturally expressed as an inactive zymogen called procaricain. The inactive form of the protease contains an inhibitory proregion which consists of an additional 106 N-terminal amino acids; the proregion is removed upon activation. The crystal structure of procaricain has been refined to 3.2 A resolution; the final model consists of three non-crystallographically related molecules. The proregion of caricain forms a separate globular domain which binds to the C-terminal domain of mature caricain. The proregion also contains an extended polypeptide chain which runs through the substrate-binding cleft, in the opposite direction to that of the substrate, and connects to the N terminus of the mature region. The mature region does not undergo any conformational change on activation. We conclude that the rate-limiting step in the in vitro activation of procaricain is the dissociation of the prodomain, which is then followed by proteolytic cleavage of the extended polypeptide chain of the proregion. The prodomain provides a stable scaffold which may facilitate the folding of the C-terminal lobe of procaricain.
- Department of Food Macromolecular Science, Institute of Food Research, Reading, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: