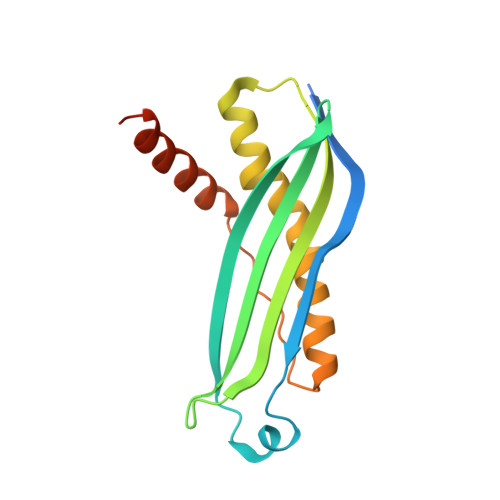
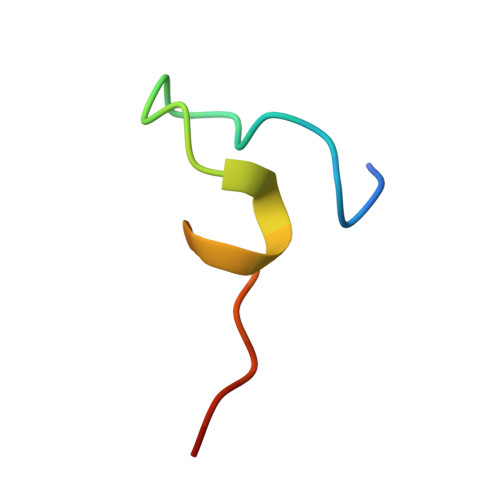
Structural determinants of SecB recognition by SecA in bacterial protein translocation
Zhou, J., Xu, Z.(2003) Nat Struct Biol 10: 942-947
- PubMed: 14517549
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb980
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OZB - PubMed Abstract:
SecB is a bacterial chaperone involved in directing pre-protein to the translocation pathway by its specific interaction with the peripheral membrane ATPase SecA. The SecB-binding site on SecA is located at its C terminus and consists of a stretch of highly conserved residues. The crystal structure of SecB in complex with the C-terminal 27 amino acids of SecA from Haemophilus influenzae shows that the SecA peptide is structured as a CCCH zinc-binding motif. One SecB tetramer is bound by two SecA peptides, and the interface involves primarily salt bridges and hydrogen bonding interactions. The structure explains the importance of the zinc-binding motif and conserved residues at the C terminus of SecA in its high-affinity binding with SecB. It also suggests a model of SecB-SecA interaction and its implication for the mechanism of pre-protein transfer in bacterial protein translocation.
- Department of Biological Chemistry and Life Sciences Institute, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor 48109-0606, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: