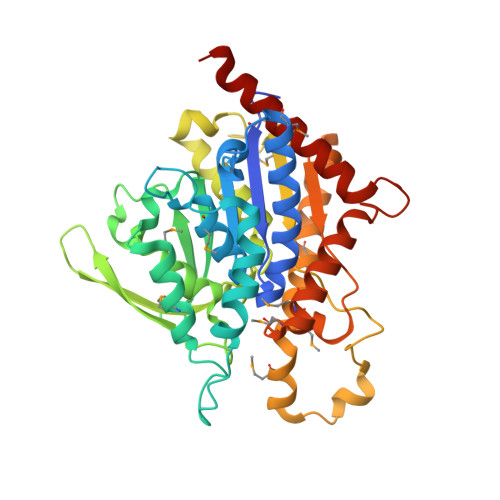
The Crystal Structure, Mutagenesis, and Activity Studies Reveal that Patatin Is a Lipid Acyl Hydrolase with a Ser-Asp Catalytic Dyad
Rydel, T.J., Williams, J.M., Krieger, E., Moshiri, F., Stallings, W.C., Brown, S.M., Pershing, J.C., Purcell, J.P., Alibhai, M.F.(2003) Biochemistry 42: 6696-6708
- PubMed: 12779324
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi027156r
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OXW - PubMed Abstract:
Patatin is a nonspecific lipid acyl hydrolase that accounts for approximately 40% of the total soluble protein in mature potato tubers, and it has potent insecticidal activity against the corn rootworm. We determined the X-ray crystal structure of a His-tagged variant of an isozyme of patatin, Pat17, to 2.2 A resolution, employing SeMet multiwavelength anomalous dispersion (MAD) phasing methods. The patatin crystal structure has three molecules in the asymmetric unit, an R-factor of 22.0%, and an R(free) of 27.2% (for 10% of the data not included in the refinement) and includes 498 water molecules. The structure notably revealed that patatin has a Ser-Asp catalytic dyad and an active site like that of human cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)) [Dessen, A., et al. (1999) Cell 97, 349-360]. In addition, patatin has a folding topology related to that of the catalytic domain of cPLA(2) and unlike the canonical alpha/beta-hydrolase fold. The structure confirms our site-directed mutagenesis and bioactivity data that initially suggested patatin possessed a Ser-Asp catalytic dyad. Alanine-scanning mutagenesis revealed that Ser77 and Asp215 were critical for both esterase and bioactivity, consistent with prior work implicating a Ser residue [Strickland, J. H., et al. (1995) Plant Physiol. 109, 667-674] and a Ser-Asp dyad [Hirschberg, H. J. H. B., et al. (2001) Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 5037-5044] in patatin's catalytic activity. The crystal structure aids the understanding of other structure-function relationships in patatin. Patatin does not display interfacial activation, a hallmark feature of lipases, and this is likely due to the fact that it lacks a flexible lid that can shield the active site.
- Monsanto Company, Chesterfield, Missouri 63017-1732, USA. timothy.j.rydel@monsanto.com
Organizational Affiliation: