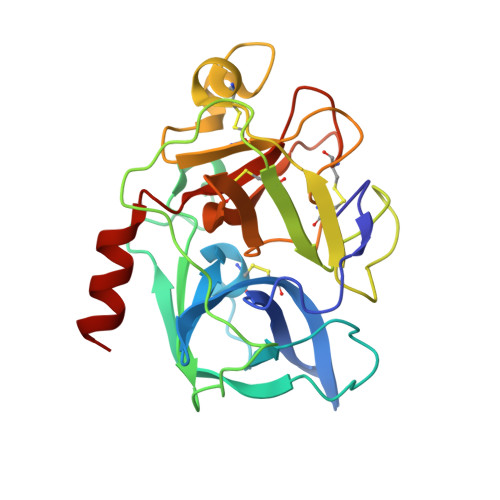
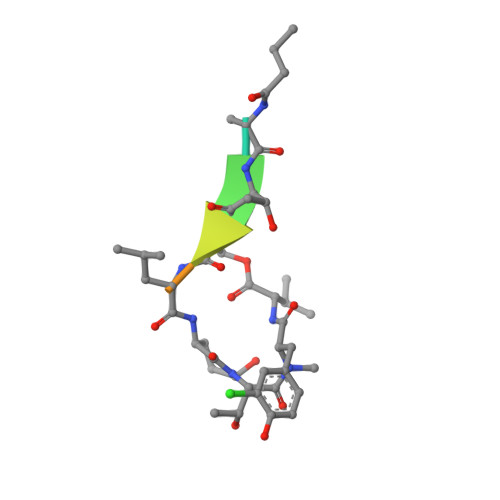
Binding Structure of Elastase Inhibitor Scyptolin A
Matern, U., Schleberger, C., Jelakovic, S., Weckesser, J., Schulz, G.E.(2003) Chem Biol 10: 997
- PubMed: 14583266
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2003.10.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OKX - PubMed Abstract:
Natural bioactive compounds are of general interest to pharmaceutical research because they may be used as leads in drug development campaigns. Among them, scyptolin A and B from Scytonema hofmanni PCC 7110 are known to inhibit porcine pancreatic elastase, which in turn resembles the attractive drug target neutrophil elastase. The crystal structure of scyptolin A as bound to pancreatic elastase was solved at 2.8 A resolution. The inhibitor occupies the most prominent subsites S1 through S4 of the elastase and prevents a hydrolytic attack by covering the active center with its rigid ring structure. The observed binding structure may help to design potent elastase inhibitors.
- Institut für Biologie II, Mikrobiologie, Albert-Ludwigs-Universität, Schänzlestrasse 1, D-79104 Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: