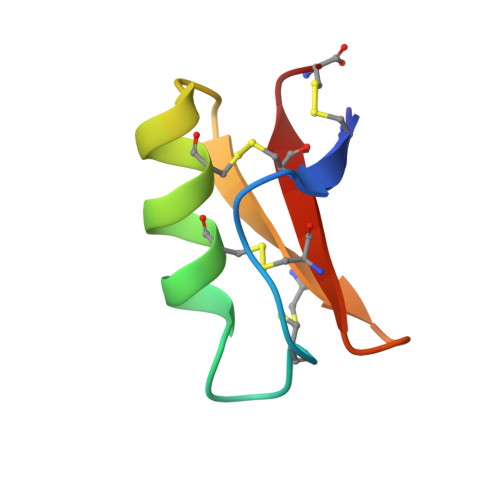
Solution structure of drosomycin, the first inducible antifungal protein from insects.
Landon, C., Sodano, P., Hetru, C., Hoffmann, J., Ptak, M.(1997) Protein Sci 6: 1878-1884
- PubMed: 9300487
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.5560060908
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MYN - PubMed Abstract:
Drosomycin is the first antifungal protein characterized recently among the broad family of inducible peptides and proteins produced by insects to respond to bacterial or septic injuries. It is a small protein of 44 amino acid residues extracted from Drosophila melanogaster that exhibits a potent activity against filamentous fungi. Its three-dimensional structure in aqueous solution was determined using 1H 2D NMR. This structure, involving an alpha-helix and a twisted three-stranded beta-sheet, is stabilized by three disulfide bridges. The corresponding Cysteine Stabilized alpha beta (CS alpha beta) motif, which was found in other defense proteins such as the antibacterial insect defensin A, short- and long-chain scorpion toxins, as well as in plant thionins and potent antifungal plant defensins, appears as remarkably persistent along evolution.
- Centre de Biophysique Moléculaire (UPR 4301 CNRS), Orléans, France.
Organizational Affiliation: