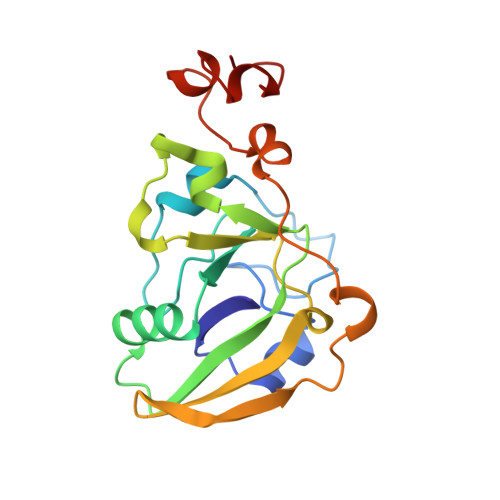
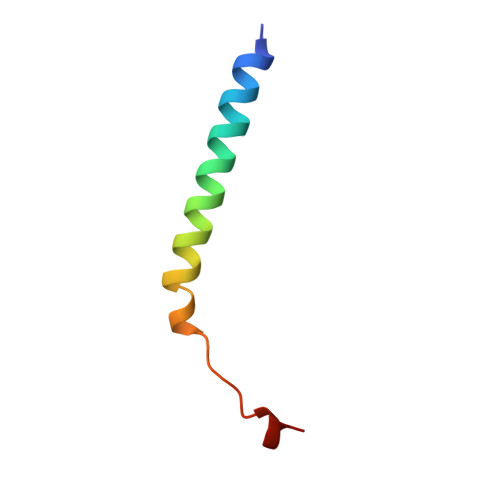
Lactose binding to heat-labile enterotoxin revealed by X-ray crystallography.
Sixma, T.K., Pronk, S.E., Kalk, K.H., van Zanten, B.A., Berghuis, A.M., Hol, W.G.(1992) Nature 355: 561-564
- PubMed: 1741035
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/355561a0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1LTT - PubMed Abstract:
Recognition of the oligosaccharide portion of ganglioside GM1 in membranes of target cells by the heat-labile enterotoxin from Escherichia coli is the crucial first step in its pathogenesis, as it is for the closely related cholera toxin. These toxins have five B subunits, which are essential for GM1 binding, and a single A subunit, which needs to be nicked by proteolysis and reduced, yielding an A1-'enzyme' and an A2-'linker' peptide. A1 is translocated across the membrane of intestinal epithelial cells, possibly after endocytosis, upon which it ADP-ribosylates the G protein Gs alpha. The mechanism of binding and translocation of these toxins has been extensively investigated, but how the protein is orientated on binding is still not clear. Knowing the precise arrangement of the ganglioside binding sites of the toxins will be useful for designing drugs against the diarrhoeal diseases caused by organisms secreting these toxins and in the development of oral vaccines against them. We present here the three-dimensional structure of the E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin complexed with lactose. This reveals the location of the binding site of the terminal galactose of GM1, which is consistent with toxin binding to the target cell with its A1 fragment pointing away from the membrane. A small helix is identified at the carboxy terminus of A2 which emerges through the central pore of the B subunits and probably comes into contact with the membrane upon binding, whereas the A1 subunit is flexible with respect to the B pentamer.
- BIOSON Research Institute, Department of Chemistry, University of Groningen, The Netherlands.
Organizational Affiliation: