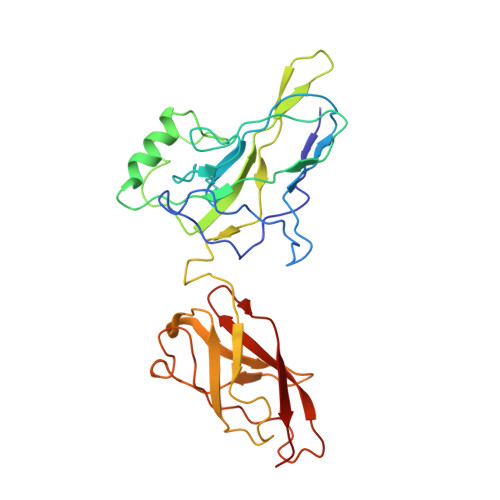
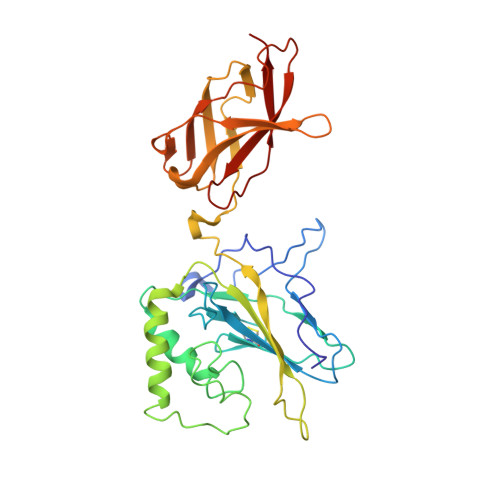
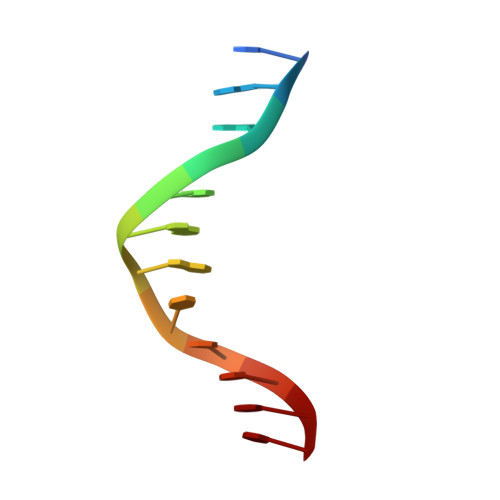
The X-ray crystal structure of the NF-kB p50/p65 heterodimer bound to the Interferon beta-kB site
Berkowitz, B., Huang, D.B., Chen-Park, F.E., Sigler, P.B., Ghosh, G.(2002) J Biological Chem 277: 24694-24700
- PubMed: 11970948
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M200006200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1LE5, 1LE9 - PubMed Abstract:
We have determined the x-ray crystal structure of the transcription factor NF-kappaB p50.p65 heterodimer complexed to kappaB DNA from the cytokine interferon beta enhancer (IFNbeta-kappaB). To better understand how the binding modes of NF-kappaB on its two best studied DNA targets might contribute to promoter-specific transcription, this structure is compared with the previously determined complex crystal structure containing NF-kappaB bound to the Ig kappa light chain gene enhancer as well as to a second NF-kappaB.Ig kappa light chain gene enhancer complex also reported in this paper. The global binding modes of all NF-kappaB.DNA complex structures are similar, although crystal-packing interactions lead to differences between identical complexes of the same crystallographic asymmetric unit. An extensive network of stacked amino acid side chains that contribute to base-specific DNA contacts is conserved among the three complexes. Consistent with earlier reports, however, the IFNbeta-kappaB DNA is bent significantly less by NF-kappaB than is the Ig kappa light chain gene enhancer. This and other small structural changes may play a role in explaining why NF-kappaB-directed transcription is sensitive to the context of specific promoters. The precise molecular mechanism behind the involvement of the high mobility group protein I(Y) in interferon beta enhanceosome formation remains elusive.
- Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06510, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: