Solution structure and stability of tryptophan-containing nucleopeptide duplexes
Gomez-Pinto, I., Marchan, V., Gago, F., Grandas, A., Gonzalez, C.(2003) Chembiochem 4: 40-49
- PubMed: 12512075
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200390012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1J9N - PubMed Abstract:
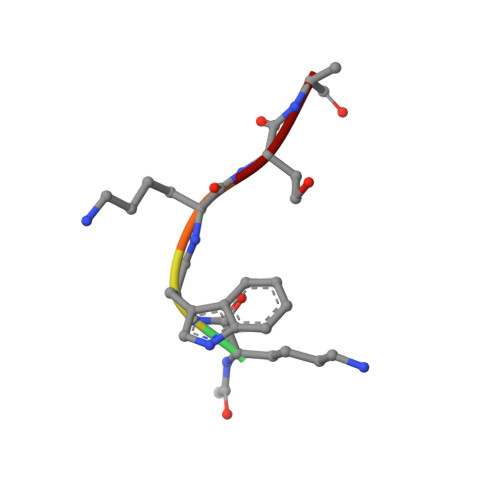
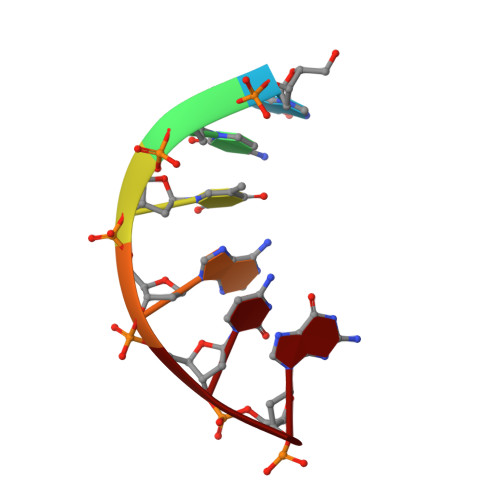
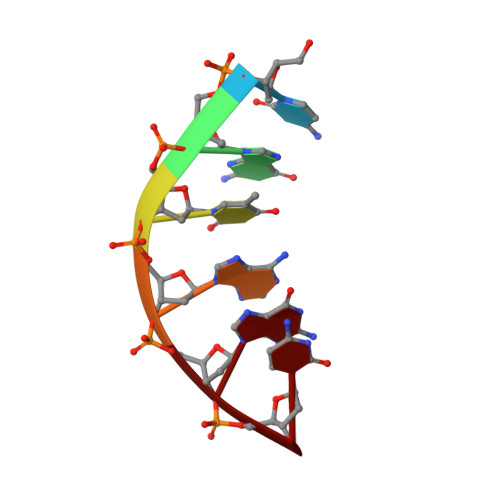
Covalently linked peptide-oligonucleotide hybrids were used as models for studying tryptophan-DNA interactions. The structure and stability of several hybrids in which peptides and oligonucleotides are linked through a phosphodiester bond between the hydroxy group of a homoserine (Hse) side chain and the 3'-end of the oligonucleotide, have been studied by both NMR and CD spectroscopy and by restrained molecular dynamics methods. The three-dimensional solution structure of the complex between Ac-Lys-Trp-Lys-Hse(p3'dGCATCG)-Ala-OH (p=phosphate, Ac=acetyl) and its complementary strand 5'dCGTAGC has been determined from a set of 276 experimental NOE distances and 33 dihedral angle constraints. The oligonucleotide structure is a well-defined duplex that belongs to the B-form family of DNA structures. The covalently linked peptide adopts a folded structure in which the tryptophan side chain stacks against the 3'-terminal guanine moiety, which forms a cap at the end of the duplex. This stacking interaction, which resembles other tryptophan-nucleobase interactions observed in some protein-DNA complexes, is not observed in the single-stranded form of Ac-Lys-Trp-Lys-Hse(p3'dGCATCG)-Ala-OH, where the peptide chain is completely disordered. A comparison with the pure DNA duplex, d(5'GCTACG3')-(5'CGTAGC3'), indicates that the interaction between the peptide and the DNA contributes to the stability of the nucleopeptide duplex. The different contributions that stabilize this complex have been evaluated by studying other nucleopeptide compounds with related sequences.
- Instituto de Química Física Rocasolano, CSIC, C/. Serrano 119, 28006 Madrid, Spain.
Organizational Affiliation: