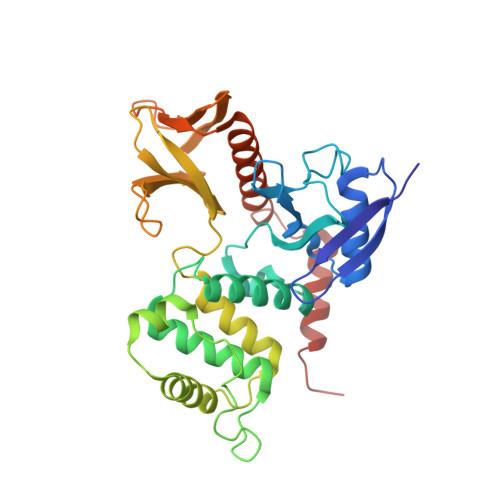
Structural basis of adhesion-molecule recognition by ERM proteins revealed by the crystal structure of the radixin-ICAM-2 complex
Hamada, K., Shimizu, T., Yonemura, S., Tsukita, S., Tsukita, S., Hakoshima, T.(2003) EMBO J 22: 502-514
- PubMed: 12554651
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg039
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1J19 - PubMed Abstract:
ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) proteins recognize the cytoplasmic domains of adhesion molecules in the formation of the membrane-associated cytoskeleton. Here we report the crystal structure of the radixin FERM (4.1 and ERM) domain complexed with the ICAM-2 cytoplasmic peptide. The non-polar region of the ICAM-2 peptide contains the RxxTYxVxxA sequence motif to form a beta-strand followed by a short 3(10)-helix. It binds the groove of the phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB)-like subdomain C mediated by a beta-beta association and several side-chain interactions. The binding mode of the ICAM-2 peptide to the FERM domain is distinct from that of the NPxY motif-containing peptide binding to the canonical PTB domain. Mutation analyses based on the crystal structure reveal the determinant elements of recognition and provide the first insights into the physical link between adhesion molecules and ERM proteins.
- Structural Biology Laboratory, Nara Institute of Science and Technology and CREST, Japan Science and Technology Corporation, 8916-5 Takayama, Ikoma, Nara 630-0101, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: