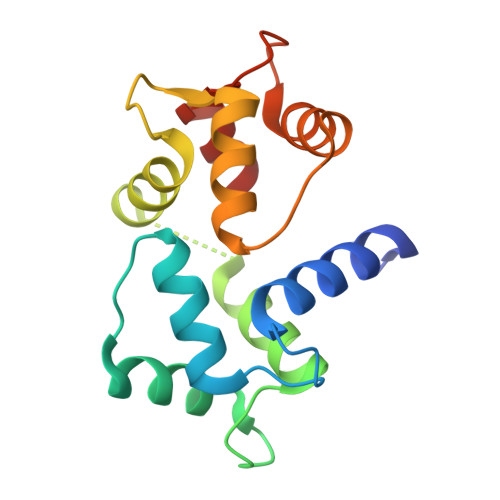
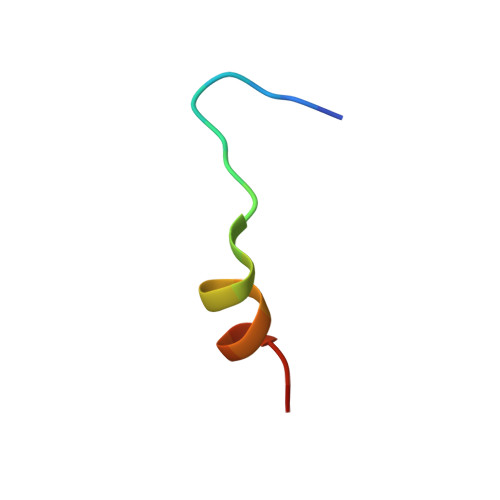
Crystal structure of a MARCKS peptide containing the calmodulin-binding domain in complex with Ca(2+)-calmodulin
Yamauchi, E., Nakatsu, T., Matsubara, M., Kato, H., Taniguchi, H.(2003) Nat Struct Biol 10: 226-231
- PubMed: 12577052
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb900
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IWQ - PubMed Abstract:
The calmodulin-binding domain of myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS), which interacts with various targets including calmodulin, actin and membrane lipids, has been suggested to function as a crosstalk point among several signal transduction pathways. We present here the crystal structure at 2 A resolution of a peptide consisting of the MARCKS calmodulin (CaM)-binding domain in complex with Ca2+-CaM. The domain assumes a flexible conformation, and the hydrophobic pocket of the calmodulin N-lobe, which is a common CaM-binding site observed in previously resolved Ca2+-CaM-target peptide complexes, is not involved in the interaction. The present structure presents a novel target-recognition mode of calmodulin and provides insight into the structural basis of the flexible interaction module of MARCKS.
- Harima Institute at SPring-8, RIKEN, 1-1-1 Kouto, Sayo, Hyogo 679-5148, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: