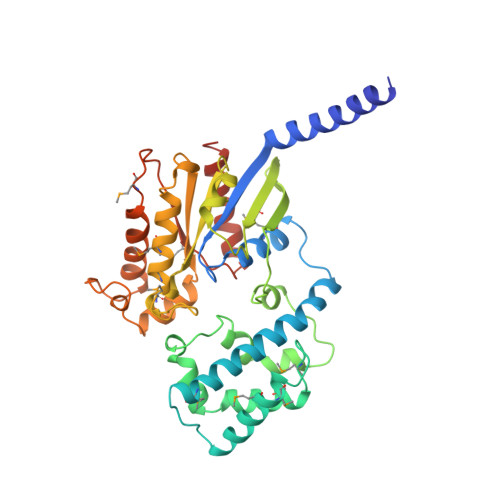
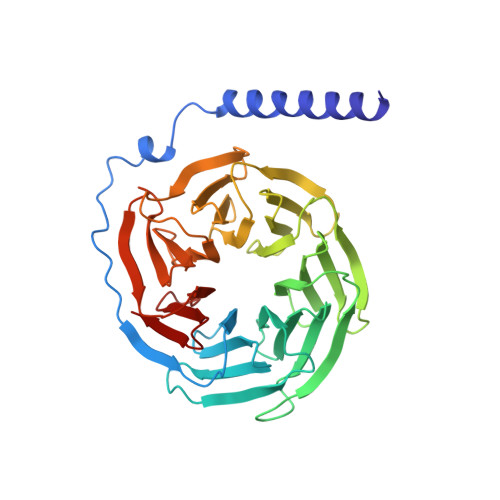
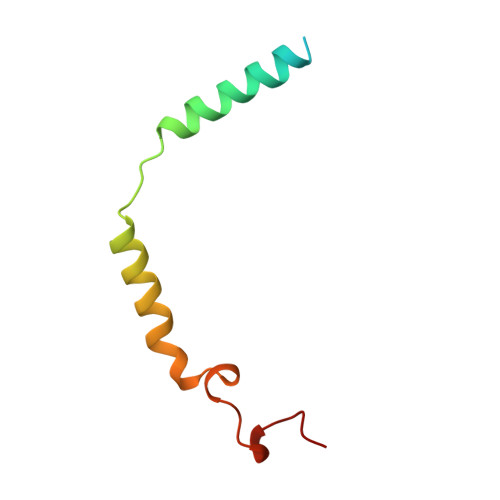
The 2.0 A crystal structure of a heterotrimeric G protein.
Lambright, D.G., Sondek, J., Bohm, A., Skiba, N.P., Hamm, H.E., Sigler, P.B.(1996) Nature 379: 311-319
- PubMed: 8552184
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/379311a0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1GOT - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of a heterotrimeric G protein reveals the mechanism of the nucleotide-dependent engagement of the alpha and beta gamma subunits that regulates their interaction with receptor and effector molecules. The interaction involves two distinct interfaces and dramatically alters the conformation of the alpha but not of the beta gamma subunits. The location of the known sites for post-translational modification and receptor coupling suggest a plausible orientation with respect to the membrane surface and an activated heptahelical receptor.
- Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06510, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: