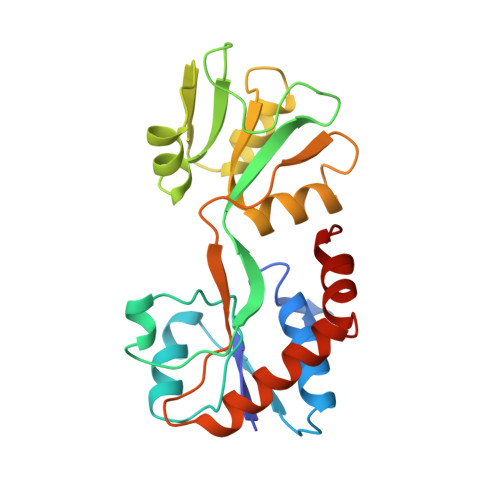
The crystal structure of glutamine-binding protein from Escherichia coli.
Hsiao, C.D., Sun, Y.J., Rose, J., Wang, B.C.(1996) J Mol Biology 262: 225-242
- PubMed: 8831790
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1996.0509
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1GGG - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of the glutamine-binding protein (GlnBP) from Escherichia coli in a ligand-free "open" conformational state has been determined by isomorphous replacement methods and refined to an R-value of 21.4% at 2.3 A resolution. There are two molecules in the asymmetric unit, related by pseudo 4-fold screw symmetry. The refined model consists of 3587 non-hydrogen atoms from 440 residues (two monomers), and 159 water molecules. The structure has root-mean-square deviations of 0.013 A from "ideal" bond lengths and 1.5 degrees from "ideal" bond angles. The GlnBP molecule has overall dimensions of approximately 60 A x 40 A x 35 A and is made up of two domains (termed large and small), which exhibit a similar supersecondary structure, linked by two antiparallel beta-strands. The small domain contains three alpha-helices and four parallel and one antiparallel beta-strands. The large domain is similar to the small domain but contains two additional alpha-helices and three more short antiparallel beta-strands. A comparison of the secondary structural motifs of GlnBP with those of other periplasmic binding proteins is discussed. A model of the "closed form" GlnBP-Gln complex has been proposed based on the crystal structures of the histidine-binding protein-His complex and "open form" GlnBP. This model has been successfully used as a search model in the crystal structure determination of the "closed form" GlnBP-Gln complex by molecular replacement methods. The model agrees remarkably well with the crystal structure of the Gln-GlnBP complex with root-mean-square deviation of 1.29 A. Our study shows that, at least in our case, it is possible to predict one conformational state of a periplasmic binding protein from another conformational state of the protein. The glutamine-binding pockets of the model and the crystal structure are compared and the modeling technique is described.
- Department of Crystallography, University of Pittsburgh, PA 15260, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: