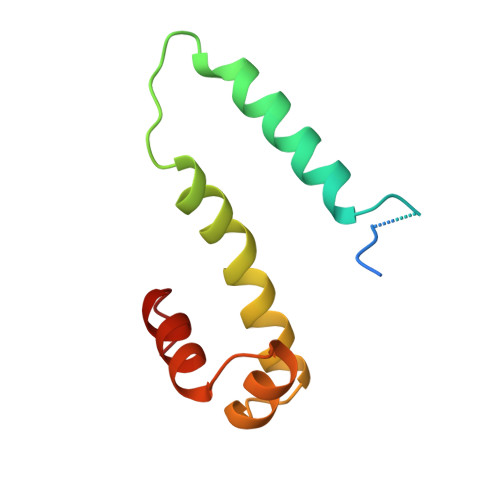
Crystal structure of the factor for inversion stimulation FIS at 2.0 A resolution.
Kostrewa, D., Granzin, J., Stock, D., Choe, H.W., Labahn, J., Saenger, W.(1992) J Mol Biology 226: 209-226
- PubMed: 1619650
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(92)90134-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1FIA - PubMed Abstract:
The factor for inversion stimulation (FIS) binds as a homodimeric molecule to a loose 15 nucleotide consensus sequence in DNA. It stimulates DNA-related processes, such as DNA inversion and excision, it activates transcription of tRNA and rRNA genes and it regulates its own synthesis. FIS crystallizes as a homodimer, with 2 x 98 amino acid residues in the asymmetric unit. The crystal structure was determined with multiple isomorphous replacement and refined to an R-factor of 19.2% against all the 12,719 X-ray data (no sigma-cutoff) extending to 2.0 A resolution. The two monomers are related by a non-crystallographic dyad axis. The structure of the dimer is modular, with the first 23 amino acid residues in molecule M1 and the first 24 in molecule M2 disordered and not "seen" in the electron density. The polypeptide folds into four alpha-helices, with alpha A, alpha A' (amino acid residues 26 to 40) and alpha B, alpha B' (49 to 69) forming the core of the FIS dimer, which is stabilized by hydrophobic forces. To the core are attached "classical" helix-turn-helix motifs, alpha C, alpha D (73 to 81 and 84 to 94) and alpha C', alpha D'. The connections linking the helices are structured by two beta-turns for alpha A/alpha B, and alpha C1 type extensions are observed at the C termini of helices alpha B, alpha C and alpha D. Helices alpha D and alpha D' contain 2 x 6 positive charges; they are separated by 24 A and can bind adjacent major grooves in B-type DNA if it is bent 90 degrees. The modular structure of FIS is also reflected by mutation experiments; mutations in the N-terminal part and alpha A interfere with FIS binding to invertases, and mutations in the helix-turn-helix motif interfere with DNA binding.
- Institut für Kristallographie, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: