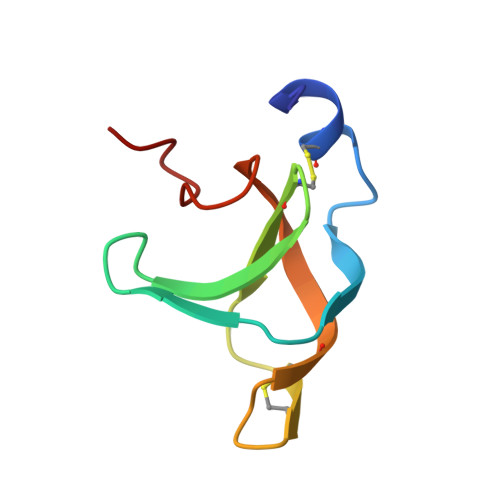
A conserved infection pathway for filamentous bacteriophages is suggested by the structure of the membrane penetration domain of the minor coat protein g3p from phage fd.
Holliger, P., Riechmann, L.(1997) Structure 5: 265-275
- PubMed: 9032075
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00184-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1FGP - PubMed Abstract:
. Gene 3 protein (g3p), a minor coat protein from bacteriophage fd mediates infection of Escherichia coli bearing an F-pilus. Its N-terminal domain (g3p-D1) is essential for infection and mediates penetration of the phage into the host cytoplasm presumbly through interaction with the Tol complex in the E. coli membranes. Structural knowledge of g3p-D1 is both important for a molecular understanding of phage infection and of biotechnological relevance, as g3p-D1 represents the primary fusion partner in phage display technology. . The solution structure of g3p-D1 was determined by NMR spectroscopy. The principal structural element of g3p-D1 is formed by a six-stranded beta barrel topologically identical to a permutated SH3 domain but capped by an additional N-terminal alpha helix. The presence of structurally similar domains in the related E. coli phages, lke and 12-2, as well as in the cholera toxin transducing phage ctxφ is indicated. The structure of g3p-D1 resembles those of the recently described PTB and PDZ domains involved in eukaryotic signal transduction. . The predicted presence of similar structures in membrane penetration domains from widely diverging filamentous phages suggests they share a conserved infection pathway. The widespread hydrogen-bond network within the beta barrel and N-terminal alpha helix in combination with two disulphide bridges renders g3p-D1 a highly stable domain, which may be important for keeping phage infective in harsh extracellular environments.
- MRC Centre for Protein Engineering, MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QH, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: