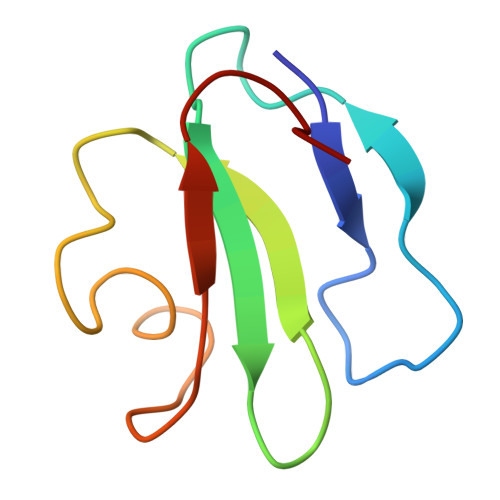
Three-dimensional solution structure of the extracellular region of the complement regulatory protein CD59, a new cell-surface protein domain related to snake venom neurotoxins.
Kieffer, B., Driscoll, P.C., Campbell, I.D., Willis, A.C., van der Merwe, P.A., Davis, S.J.(1994) Biochemistry 33: 4471-4482
- PubMed: 7512825
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ERG, 1ERH - PubMed Abstract:
The cell surface antigen CD59 is an inhibitor of complement-mediated lysis and a member of the Ly6 superfamily (Ly6SF) of cysteine-rich cell-surface molecules whose sequences are related to those of snake venom neurotoxins. The three-dimensional solution structure of a recombinant form of the extracellular region of the molecule (residues 1-70 of the mature protein; sCD59) has been solved by 2D NMR methods. sCD59 is a relatively flat, disk-shaped molecule consisting of a two-standed beta-sheet finger loosely packed against a protein core formed by a three-stranded beta-sheet and a short helix. Structure calculations allowed an unambiguous assignment of the disulfide-bonded cysteine pairs as 3-26, 6-13, 19-39, 45-63, and 64-69. The topology of sCD59 is similar to that of the snake venom neurotoxins and consistent with an evolutionary relationship existing between the Ly6SF and the neurotoxins.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford, U.K.
Organizational Affiliation: