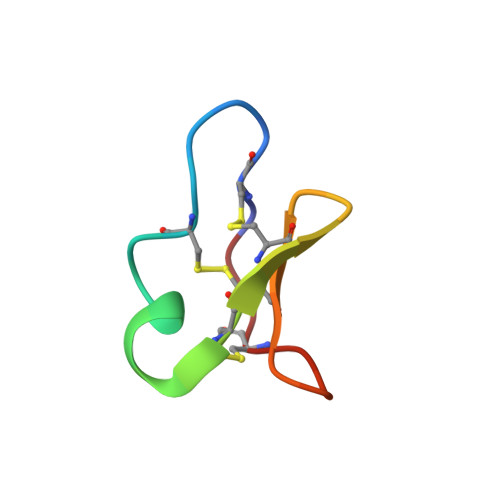
Plant cyclotides: A unique family of cyclic and knotted proteins that defines the cyclic cystine knot structural motif.
Craik, D.J., Daly, N.L., Bond, T., Waine, C.(1999) J Mol Biology 294: 1327-1336
- PubMed: 10600388
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1999.3383
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1DF6 - PubMed Abstract:
Several macrocyclic peptides ( approximately 30 amino acids), with diverse biological activities, have been isolated from the Rubiaceae and Violaceae plant families over recent years. We have significantly expanded the range of known macrocyclic peptides with the discovery of 16 novel peptides from extracts of Viola hederaceae, Viola odorata and Oldenlandia affinis. The Viola plants had not previously been examined for these peptides and thus represent novel species in which these unusual macrocyclic peptides are produced. Further, we have determined the three-dimensional structure of one of these novel peptides, cycloviolacin O1, using (1)H NMR spectroscopy. The structure consists of a distorted triple-stranded beta-sheet and a cystine-knot arrangement of the disulfide bonds. This structure is similar to kalata B1 and circulin A, the only two macrocyclic peptides for which a structure was available, suggesting that despite the sequence variation throughout the peptides they form a family in which the overall fold is conserved. We refer to these peptides as the cyclotide family and their embedded topology as the cyclic cystine knot (CCK) motif. The unique cyclic and knotted nature of these molecules makes them a fascinating example of topologically complex proteins. Examination of the sequences reveals they can be separated into two subfamilies, one of which tends to contain a larger number of positively charged residues and has a bracelet-like circularization of the backbone. The second subfamily contains a backbone twist due to a cis-Pro peptide bond and may conceptually be regarded as a molecular Moebius strip. Here we define the structural features of the two apparent subfamilies of the CCK peptides which may be significant for the likely defense related role of these peptides within plants.
- Centre for Drug Design and Development, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, QLD 4072, Australia. d.craik@mailbox.uq.edu.au
Organizational Affiliation: