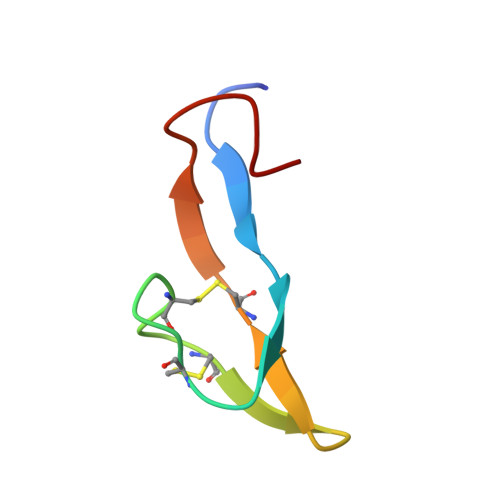
Solution structure of bromelain inhibitor IV from pineapple stem: structural similarity with Bowman-Birk trypsin/chymotrypsin inhibitor from soybean.
Hatano, K., Kojima, M., Tanokura, M., Takahashi, K.(1996) Biochemistry 35: 5379-5384
- PubMed: 8611527
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi952754+
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1BI6, 2BI6 - PubMed Abstract:
Bromelain inhibitor VI from pineapple stem (BI-VI) is a unique double-chain inhibitor with an 11-residue light chain and a 41-residue heavy chain by disulfide bonds and inhibits the cysteine proteinase bromelain competitively. The structure of BI-VI in aqueous solution was determined using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and simulated annealing-based calculations. Its three-dimensional structure was shown to be composed of two distinct domains, each of which is formed by a three-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet. Unexpectedly, BI-VI was found to share a similar folding and disulfide bond connectivities not with cystatin superfamily inhibitors which inhibit the same cysteine proteinases but with the Bowman-Birk trypsin/chymotrypsin inhibitor from soybean (BBI-I). BBI-I is a 71-residue inhibitor which has two independent inhibitory sites toward the serine proteinases trypsin and chymotrypsin. These structural similarities with BBI-I suggest that they have evolved from a common ancestor and differentiated in function during a course of molecular evolution.
- Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, University of Tokyo, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: