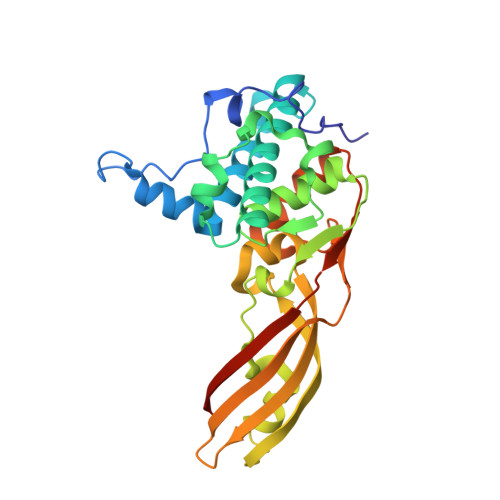
Crystal structure of colicin M, a novel phosphatase specifically imported by Escherichia coli
Zeth, K., Romer, C., Patzer, S.I., Braun, V.(2008) J Biol Chem 283: 25324-25331
- PubMed: 18640984
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M802591200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DA3, 3DA4 - PubMed Abstract:
Colicins are cytotoxic proteins secreted by certain strains of Escherichia coli. Colicin M is unique among these toxins in that it acts in the periplasm and specifically inhibits murein biosynthesis by hydrolyzing the pyrophosphate linkage between bactoprenol and the murein precursor. We crystallized colicin M and determined the structure at 1.7A resolution using x-ray crystallography. The protein has a novel structure composed of three domains with distinct functions. The N-domain is a short random coil and contains the exposed TonB box. The central domain includes a hydrophobic alpha-helix and binds presumably to the FhuA receptor. The C-domain is composed of a mixed alpha/beta-fold and forms the phosphatase. The architectures of the individual modules show no similarity to known structures. Amino acid replacements in previously isolated inactive colicin M mutants are located in the phosphatase domain, which contains a number of surface-exposed residues conserved in predicted bacteriocins of other bacteria. The novel phosphatase domain displays no sequence similarity to known phosphatases. The N-terminal and central domains are not conserved among bacteriocins, which likely reflect the distinct import proteins required for the uptake of the various bacteriocins. The homology pattern supports our previous proposal that colicins evolved by combination of distinct functional domains.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, Department of Protein Evolution, D-72076 Tübingen, Germany.