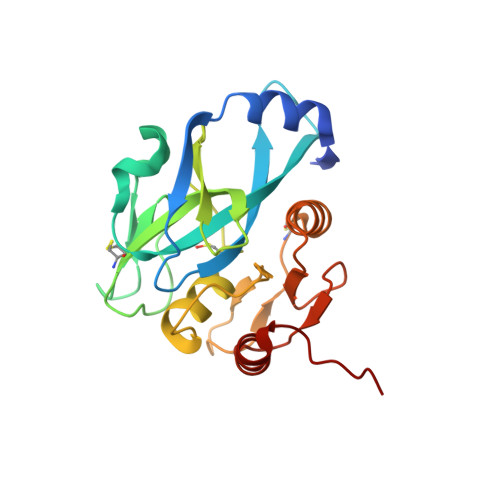
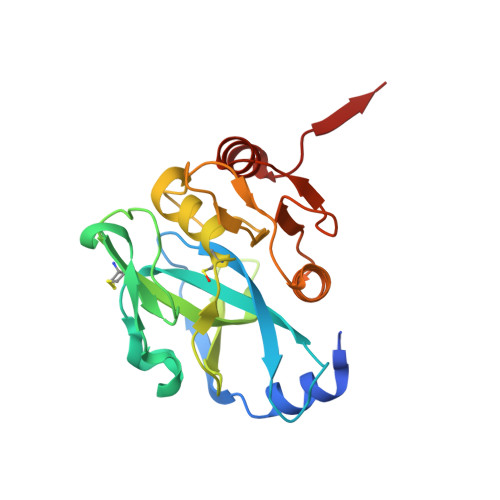
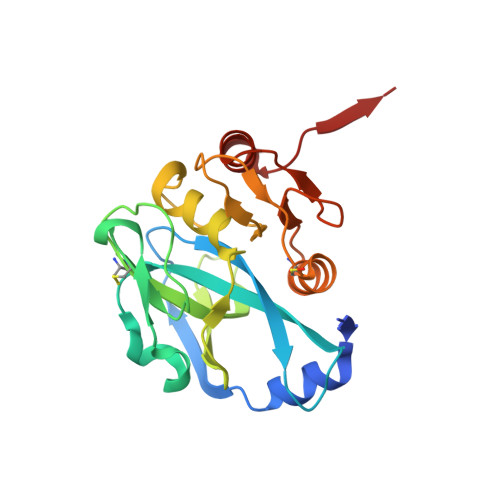
Crystal Structures of Yellowtail Ascites Virus VP4 Protease: TRAPPING AN INTERNAL CLEAVAGE SITE TRANS ACYL-ENZYME COMPLEX IN A NATIVE SER/LYS DYAD ACTIVE SITE.
Chung, I.Y., Paetzel, M.(2013) J Biol Chem 288: 13068-13081
- PubMed: 23511637
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.386953
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4IZJ, 4IZK - PubMed Abstract:
Yellowtail ascites virus (YAV) is an aquabirnavirus that causes ascites in yellowtail, a fish often used in sushi. Segment A of the YAV genome codes for a polyprotein (pVP2-VP4-VP3), where processing by its own VP4 protease yields the capsid protein precursor pVP2, the ribonucleoprotein-forming VP3, and free VP4. VP4 protease utilizes the rarely observed serine-lysine catalytic dyad mechanism. Here we have confirmed the existence of an internal cleavage site, preceding the VP4/VP3 cleavage site. The resulting C-terminally truncated enzyme (ending at Ala(716)) is active, as shown by a trans full-length VP4 cleavage assay and a fluorometric peptide cleavage assay. We present a crystal structure of a native active site YAV VP4 with the internal cleavage site trapped as trans product complexes and trans acyl-enzyme complexes. The acyl-enzyme complexes confirm directly the role of Ser(633) as the nucleophile. A crystal structure of the lysine general base mutant (K674A) reveals the acyl-enzyme and empty binding site states of VP4, which allows for the observation of structural changes upon substrate or product binding. These snapshots of three different stages in the VP4 protease reaction mechanism will aid in the design of anti-birnavirus compounds, provide insight into previous site-directed mutagenesis results, and contribute to understanding of the serine-lysine dyad protease mechanism. In addition, we have discovered that this protease contains a channel that leads from the enzyme surface (adjacent to the substrate binding groove) to the active site and the deacylating water.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, British Columbia V5A 1S6, Canada.