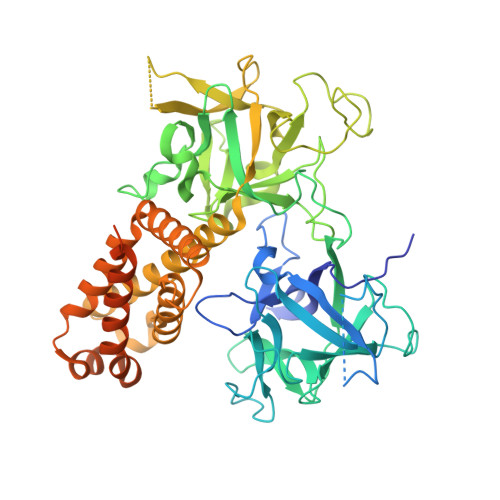
Structural insights into the human RyR2 N-terminal region involved in cardiac arrhythmias.
Borko, L., Bauerova-Hlinkova, V., Hostinova, E., Gasperik, J., Beck, K., Lai, F.A., Zahradnikova, A., Sevcik, J.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 2897-2912
- PubMed: 25372681
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714020343
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JKQ - PubMed Abstract:
Human ryanodine receptor 2 (hRyR2) mediates calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, enabling cardiomyocyte contraction. The N-terminal region of hRyR2 (amino acids 1-606) is the target of >30 arrhythmogenic mutations and contains a binding site for phosphoprotein phosphatase 1. Here, the solution and crystal structures determined under near-physiological conditions, as well as a homology model of the hRyR2 N-terminal region, are presented. The N-terminus is held together by a unique network of interactions among its three domains, A, B and C, in which the central helix (amino acids 410-437) plays a prominent stabilizing role. Importantly, the anion-binding site reported for the mouse RyR2 N-terminal region is notably absent from the human RyR2. The structure concurs with the differential stability of arrhythmogenic mutations in the central helix (R420W, I419F and I419F/R420W) which are owing to disparities in the propensity of mutated residues to form energetically favourable or unfavourable contacts. In solution, the N-terminus adopts a globular shape with a prominent tail that is likely to involve residues 545-606, which are unresolved in the crystal structure. Docking the N-terminal domains into cryo-electron microscopy maps of the closed and open RyR1 conformations reveals C(α) atom movements of up to 8 Å upon channel gating, and predicts the location of the leucine-isoleucine zipper segment and the interaction site for spinophilin and phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 on the RyR surface.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Structural Biology, Institute of Molecular Biology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Dúbravská cesta 21, 845 51 Bratislava, Slovakia.