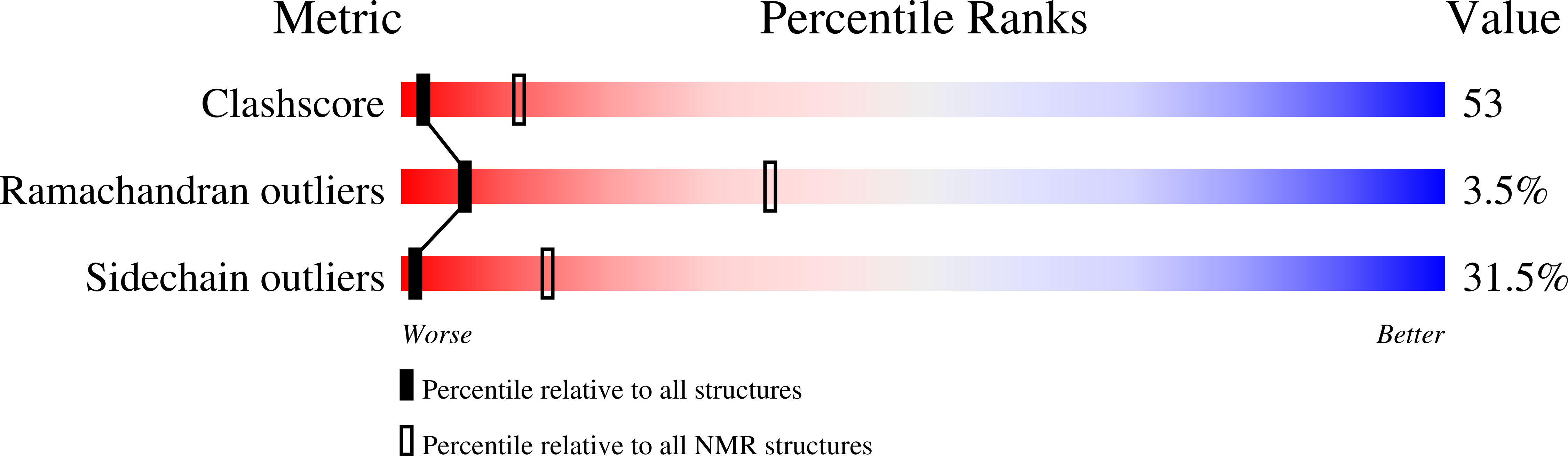Characterization of two distinct modes of drug binding to human intestinal Fatty Acid binding protein.
Patil, R., Laguerre, A., Wielens, J., Headey, S.J., Williams, M.L., Hughes, M.L., Mohanty, B., Porter, C.J., Scanlon, M.J.(2014) ACS Chem Biol 9: 2526-2534
- PubMed: 25144524
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cb5005178
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MJI - PubMed Abstract:
The aqueous cytoplasm of cells poses a potentially significant barrier for many lipophilic drugs to reach their sites of action. Fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) bind to poorly water-soluble fatty acids (FAs) and lipophilic compounds and facilitate their intracellular transport. Several structures of FA in complex with FABPs have been described, but data describing the binding sites of other lipophilic ligands including drugs are limited. Here the environmentally sensitive fluorophores, 1-anilinonapthalene 8-sulfonic acid (ANS), and 11-dansylamino undecanoic acid (DAUDA) were used to investigate drug binding to human intestinal FABP (hIFABP). Most drugs that bound hIFABP were able to displace both ANS and DAUDA. A notable exception was ketorolac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that bound to hIFABP and displaced DAUDA but failed to displace ANS. Isothermal titration calorimetry revealed that for the majority of ligands including FA, ANS, and DAUDA, binding to hIFABP was exothermic. In contrast, ketorolac binding to hIFABP was endothermic and entropy-driven. The X-ray crystal structure of DAUDA-hIFABP revealed a FA-like binding mode where the carboxylate of DAUDA formed a network of hydrogen bonds with residues at the bottom of the binding cavity and the dansyl group interacted with residues in the portal region. In contrast, NMR chemical shift perturbation (CSP) data suggested that ANS bound only toward the bottom of the hIFABP cavity, whereas ketorolac occupied only the portal region. The CSP data further suggested that ANS and ketorolac were able to bind simultaneously to hIFABP, consistent with the lack of displacement of ANS observed by fluorescence and supported by a model of the ternary complex. The NMR solution structure of the ketorolac-hIFABP complex therefore describes a newly characterized, hydrophobic ligand binding site in the portal region of hIFABP.
Organizational Affiliation:
Medicinal Chemistry, Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences and ∥Drug Delivery, Disposition and Dynamics, Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Monash University , 381 Royal Parade, Parkville, Victoria 3052, Australia.