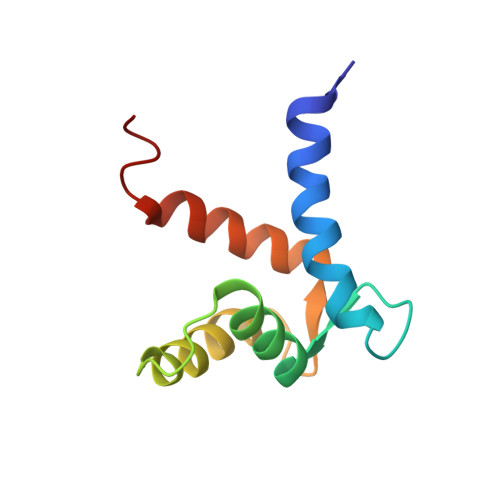
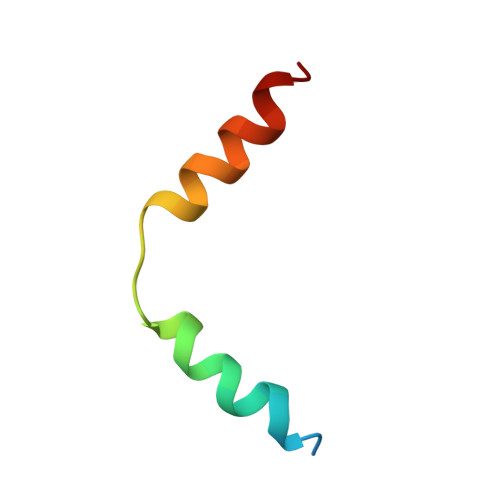
Structure of the S100A6 complex with a fragment from the C-terminal domain of Siah-1 interacting protein: a novel mode for S100 protein target recognition.
Lee, Y.T., Dimitrova, Y.N., Schneider, G., Ridenour, W.B., Bhattacharya, S., Soss, S.E., Caprioli, R.M., Filipek, A., Chazin, W.J.(2008) Biochemistry 47: 10921-10932
- PubMed: 18803400
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi801233z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2JTT - PubMed Abstract:
S100A6 is a member of the S100 subfamily of EF-hand Ca (2+) binding proteins that has been shown to interact with calcyclin binding protein/Siah-1 interacting protein (CacyBP/SIP or SIP), a subunit of an SCF-like E3 ubiquitin ligase complex (SCF-TBL1) formed under genotoxic stress. SIP serves as a scaffold in this complex, linking the E2-recruiting module Siah-1 to the substrate-recruiting module Skp1-TBL1. A cell-based functional assay suggests that S100A6 modulates the activity of SCF-TBL1. The results from the cell-based experiments could be enhanced if it were possible to selectively inhibit S100A6-SIP interactions without perturbing any other functions of the two proteins. To this end, the structure of the S100A6-SIP complex was determined in solution by NMR and the strength of the interaction was characterized by isothermal titration calorimetry. In an initial step, the minimal S100A6 binding region in SIP was mapped to a 31-residue fragment (Ser189-Arg219) in the C-terminal domain. The structure of the S100A6-SIP(189-219) complex revealed that SIP(189-219) forms two helices, the first of which (Met193-Tyr200) interacts with S100A6 in a canonical binding mode. The second helix (Met207-Val216) lies over the S100A6 dimer interface, a mode of binding to S100A6 that has not previously been observed for any target bound to an S100 protein. A series of structure-based SIP mutations showed reduced S100A6 binding affinity, setting the stage for direct functional analysis of S100A6-SIP interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departments of Biochemistry and Chemistry and Center for Structural Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee 37232-8725, USA.