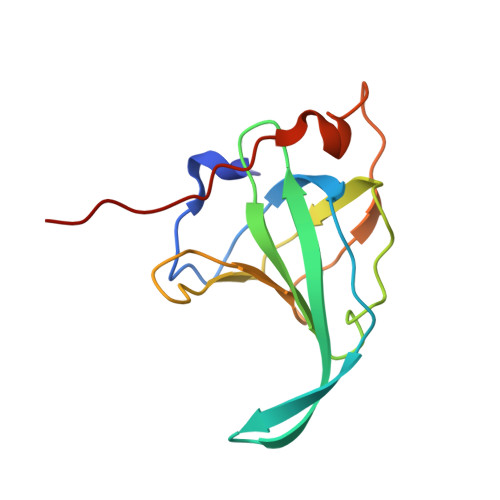
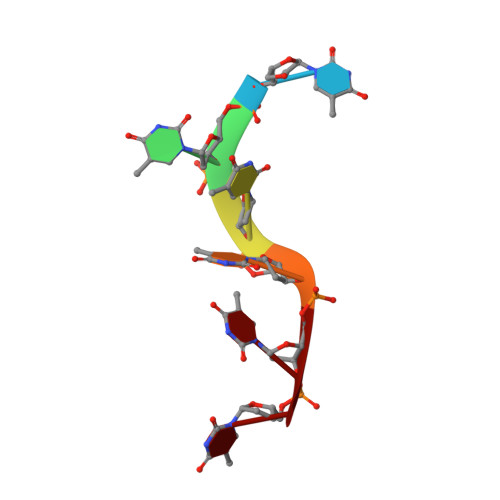
The structural basis of DNA binding by the single-stranded DNA-binding protein from Sulfolobus solfataricus
Gamsjaeger, R., Kariawasam, R., Gimenez, A.X., Touma, C., McIlwain, E., Bernardo, R.E., Shepherd, N.E., Ataide, S.F., Dong, Q., Richard, D.J., White, M.F., Cubeddu, L.(2015) Biochem J 465: 337-346
- PubMed: 25367669
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20141140
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MNA - PubMed Abstract:
Canonical single-stranded DNA-binding proteins (SSBs) from the oligosaccharide/oligonucleotide-binding (OB) domain family are present in all known organisms and are critical for DNA replication, recombination and repair. The SSB from the hyperthermophilic crenarchaeote Sulfolobus solfataricus (SsoSSB) has a 'simple' domain organization consisting of a single DNA-binding OB fold coupled to a flexible C-terminal tail, in contrast with other SSBs in this family that incorporate up to four OB domains. Despite the large differences in the domain organization within the SSB family, the structure of the OB domain is remarkably similar all cellular life forms. However, there are significant differences in the molecular mechanism of ssDNA binding. We have determined the structure of the SsoSSB OB domain bound to ssDNA by NMR spectroscopy. We reveal that ssDNA recognition is modulated by base-stacking of three key aromatic residues, in contrast with the OB domains of human RPA and the recently discovered human homologue of SsoSSB, hSSB1. We also demonstrate that SsoSSB binds ssDNA with a footprint of five bases and with a defined binding polarity. These data elucidate the structural basis of DNA binding and shed light on the molecular mechanism by which these 'simple' SSBs interact with ssDNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
*School of Science and Health, University of Western Sydney, Penrith, NSW 2751, Australia.