The FKBP-Type Domain of the Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Interacting Protein Reveals an Unusual Hsp90 Interaction.
Linnert, M., Lin, Y.J., Manns, A., Haupt, K., Paschke, A.K., Fischer, G., Weiwad, M., Luecke, C.(2013) Biochemistry 52: 2097-2107
- PubMed: 23418784
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi301649m
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LKN - PubMed Abstract:
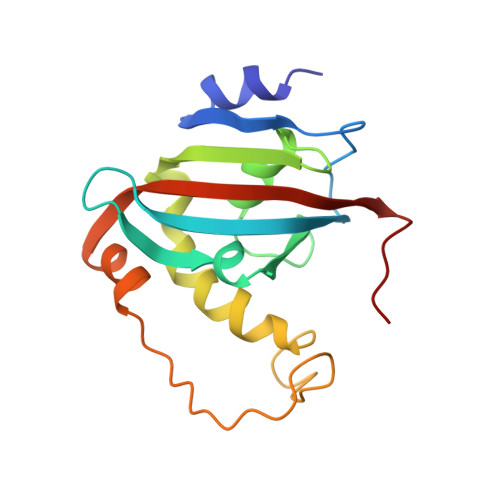
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor-interacting protein (AIP) has been predicted to consist of an N-terminal FKBP-type peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase (PPIase) domain and a C-terminal tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain, as typically found in FK506-binding immunophilins. AIP, however, exhibited no inherent FK506 binding or PPIase activity. Alignment with the prototypic FKBP12 showed a high sequence homology but indicated inconsistencies with regard to the secondary structure prediction derived from chemical shift analysis of AIP(2-166). NMR-based structure determination of AIP(2-166) now revealed a typical FKBP fold with five antiparallel β-strands forming a half β-barrel wrapped around a central α-helix, thus permitting AIP to be also named FKBP37.7 according to FKBP nomenclature. This PPIase domain, however, features two structure elements that are unusual for FKBPs: (i) an N-terminal α-helix, which additionally stabilizes the domain, and (ii) a rather long insert, which connects the last two β-strands and covers the putative active site. Diminution of the latter insert did not generate PPIase activity or FK506 binding capability, indicating that the lack of catalytic activity in AIP is the result of structural differences within the PPIase domain. Compared to active FKBPs, a diverging conformation of the loop connecting β-strand C' and the central α-helix apparently is responsible for this inherent lack of catalytic activity in AIP. Moreover, Hsp90 was identified as potential physiological interaction partner of AIP, which revealed binding contacts not only at the TPR domain but uncommonly also at the PPIase domain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max Planck Research Unit for Enzymology of Protein Folding , Weinbergweg 22, 06120 Halle (Saale), Germany.