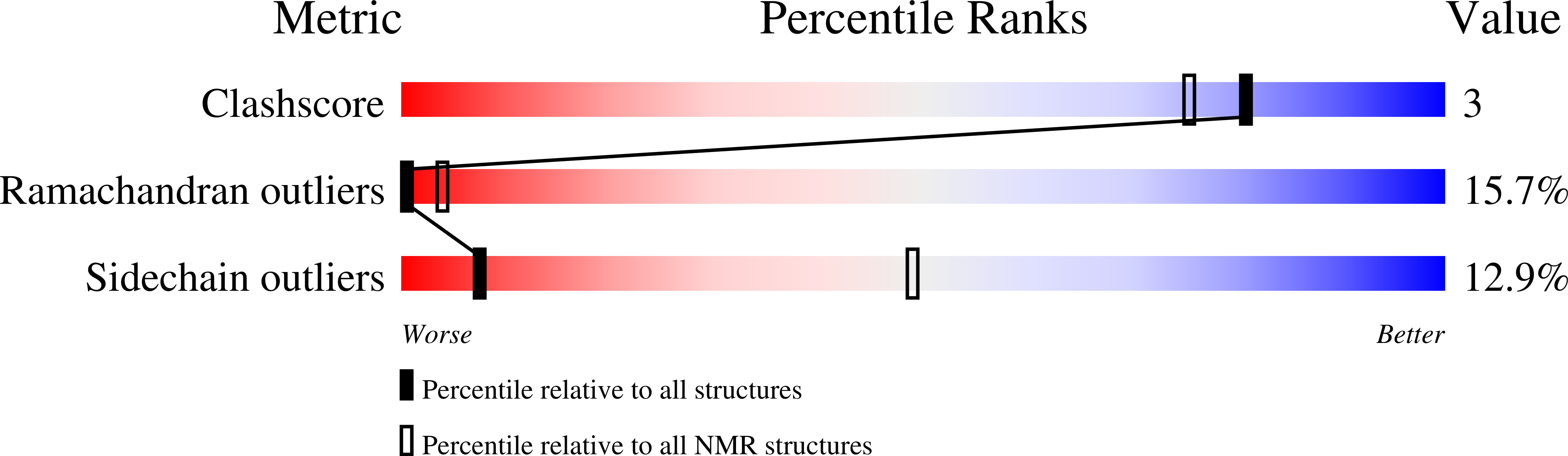A vitellogenin polyserine cleavage site: highly disordered conformation protected from proteolysis by phosphorylation.
Havukainen, H., Underhaug, J., Wolschin, F., Amdam, G., Halskau, O.(2012) J Exp Biol 215: 1837-1846
- PubMed: 22573762
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.065623
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LIC, 2LID - PubMed Abstract:
Vitellogenin (Vg) is an egg-yolk precursor protein in most oviparous species. In honeybee (Apis mellifera), the protein (AmVg) also affects social behavior and life-span plasticity. Despite its manifold functions, the AmVg molecule remains poorly understood. The subject of our structure-oriented AmVg study is its polyserine tract - a little-investigated repetitive protein segment mostly found in insects. We previously reported that AmVg is tissue specifically cleaved in the vicinity of this tract. Here, we show that, despite its potential for an open, disordered structure, AmVg is unexpectedly resistant to trypsin/chymotrypsin digestion at the tract. Our findings suggest that multiple phosphorylation plays a role in this resilience. Sequence variation is highly pronounced at the polyserine region in insect Vgs. We demonstrate that sequence differences in this region can lead to structural variation, as NMR and circular dichroism (CD) evidence assign different conformational propensities to polyserine peptides from the honeybee and the jewel wasp Nasonia vitripennis; the former is extended and disordered and the latter more compact and helical. CD analysis of the polyserine region of bumblebee Bombus ignitus and wasp Pimpla nipponica supports a random coil structure in these species. The spectroscopic results strengthen our model of the AmVg polyserine tract as a flexible domain linker shielded by phosphorylation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Biotechnology and Food Science, Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Aas, Norway. heli.havukainen@umb.no