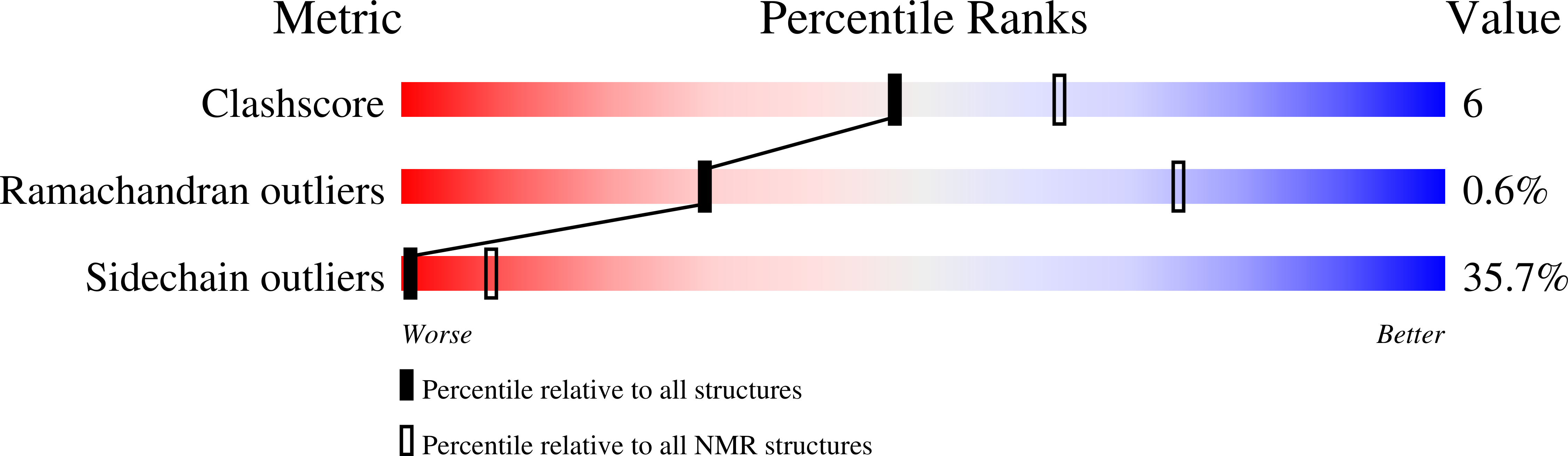A disulfide bridge network within the soluble periplasmic domain determines structure and function of the outer membrane protein RCSF.
Rogov, V.V., Rogova, N.Y., Bernhard, F., Lohr, F., Dotsch, V.(2011) J Biol Chem 286: 18775-18783
- PubMed: 21471196
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.230185
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2L8Y - PubMed Abstract:
RcsF, a proposed auxiliary regulator of the regulation of capsule synthesis (rcs) phosphorelay system, is a key element for understanding the RcsC-D-A/B signaling cascade, which is responsible for the regulation of more than 100 genes and is involved in cell division, motility, biofilm formation, and virulence. The RcsC-D-A/B system is one of the most complex bacterial signal transduction pathways, consisting of several membrane-bound and soluble proteins. RcsF is a lipoprotein attached to the outer membrane and plays an important role in activating the RcsC-d-A/B pathway. The exact mechanism of activation of the rcs phosphorelay by RcsF, however, remains unknown. We have analyzed the sequence of RcsF and identified three structural elements: 1) an N-terminal membrane-anchored helix (residues 3-13), 2) a loop (residues 14-48), and 3) a C-terminal folded domain (residues 49-134). We have determined the structure of this C-terminal domain and started to investigate its interaction with potential partners. Important features of its structure are two disulfide bridges between Cys-74 and Cys-118 and between Cys-109 and Cys-124. To evaluate the importance of this RcsF disulfide bridge network in vivo, we have examined the ability of the full-length protein and of specific Cys mutants to initiate the rcs signaling cascade. The results indicate that the Cys-74/Cys-118 and the Cys-109/Cys-124 residues correlate pairwise with the activity of RcsF. Interaction studies showed a weak interaction with an RNA hairpin. However, no interaction could be detected with reagents that are believed to activate the rcs phosphorelay, such as lysozyme, glucose, or Zn(2+) ions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biophysical Chemistry and Center for Biomolecular Magnetic Resonance, Goethe University, 60438 Frankfurt/Main, Germany.