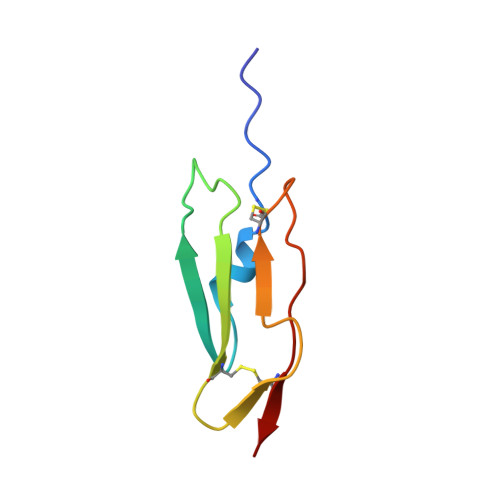
Structural analysis of the complement control protein (CCP) modules of GABA(B) receptor 1a: only one of the two CCP modules is compactly folded.
Blein, S., Ginham, R., Uhrin, D., Smith, B.O., Soares, D.C., Veltel, S., McIlhinney, R.A., White, J.H., Barlow, P.N.(2004) J Biol Chem 279: 48292-48306
- PubMed: 15304491
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M406540200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SRZ, 1SS2 - PubMed Abstract:
The gamma-aminobutyric acid type B (GABA(B)) receptor is a heterodimeric G-protein-coupled receptor. In humans, three splice variants of the GABA(B) receptor 1 (R1) subunit differ in having one, both, or neither of two putative complement control protein (CCP) modules at the extracellular N terminus, prior to the GABA-binding domain. The in vivo function of these predicted modules remains to be discovered, but a likely association with extracellular matrix proteins is intriguing. The portion of the GABA(B) R1a variant encompassing both of its CCP module-like sequences has been expressed, as have the sequences corresponding to each individual module. Each putative CCP module exhibits the expected pattern of disulfide formation. However, the second module (CCP2) is more compactly folded than the first, and the three-dimensional structure of this more C-terminal module (expressed alone) was solved on the basis of NMR-derived nuclear Overhauser effects. This revealed a strong similarity to previously determined CCP module structures in the regulators of complement activation. The N-terminal module (CCP1) displayed conformational heterogeneity under a wide range of conditions whether expressed alone or together with CCP2. Several lines of evidence indicated the presence of native disorder in CCP1, despite the fact that recombinant CCP1 contributes to binding to the extracellular matrix protein fibulin-2. Thus, we have shown that the two CCP modules of GABA(B) R1a have strikingly different structural properties, reflecting their different functions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Edinburgh Protein Interaction Centre, University of Edinburgh, West Mains Road, Edinburgh EH9 3JJ, Scotland, United Kingdom.