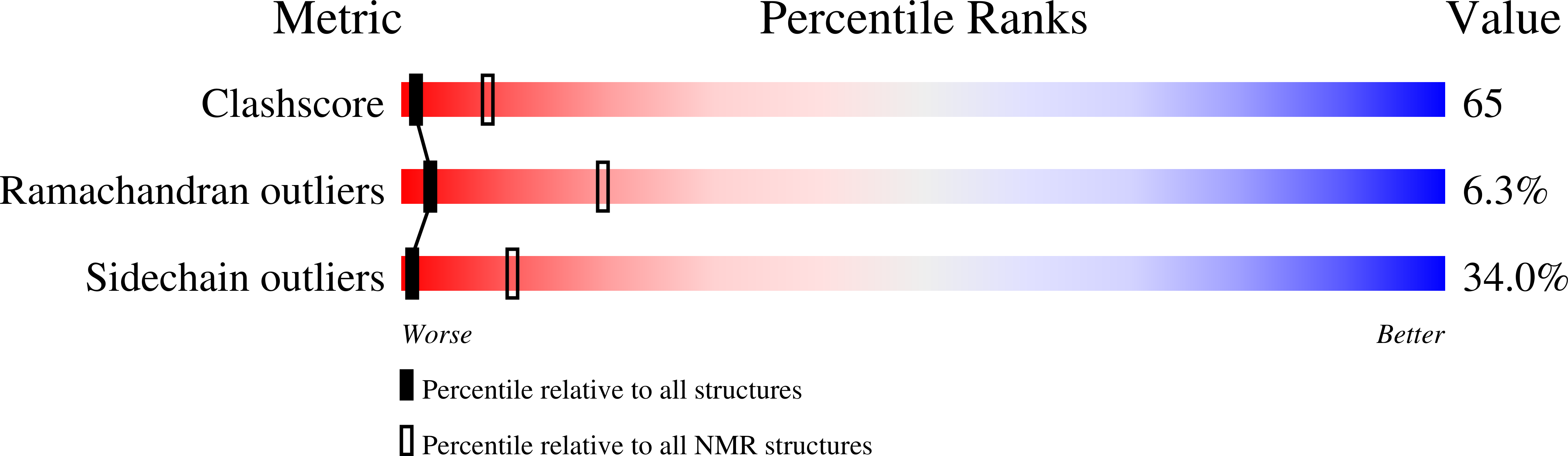Electrostatic properties of the structure of the docking and dimerization domain of protein kinase A IIalpha
Morikis, D., Roy, M., Newlon, M.G., Scott, J.D., Jennings, P.A.(2002) Eur J Biochem 269: 2040-2051
- PubMed: 11985580
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02852.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1L6E - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of the N-terminal docking and dimerization domain of the type IIalpha regulatory subunit (RIIalpha D/D) of protein kinase A (PKA) forms a noncovalent stand-alone X-type four-helix bundle structural motif, consisting of two helix-loop-helix monomers. RIIalpha D/D possesses a strong hydrophobic core and two distinct, exposed faces. A hydrophobic face with a groove is the site of protein-protein interactions necessary for subcellular localization. A highly charged face, opposite to the former, may be involved in regulation of protein-protein interactions as a result of changes in phosphorylation state of the regulatory subunit. Although recent studies have addressed the hydrophobic character of packing of RIIalpha D/D and revealed the function of the hydrophobic face as the binding site to A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs), little attention has been paid to the charges involved in structure and function. To examine the electrostatic character of the structure of RIIalpha D/D we have predicted mean apparent pKa values, based on Poisson-Boltzmann electrostatic calculations, using an ensemble of calculated dimer structures. We propose that the helix promoting sequence Glu34-X-X-X-Arg38 stabilizes the second helix of each monomer, through the formation of a (i, i +4) side chain salt bridge. We show that a weak inter-helical hydrogen bond between Tyr35-Glu19 of each monomer contributes to tertiary packing and may be responsible for discriminating from alternative quaternary packing of the two monomers. We also show that an inter-monomer hydrogen bond between Asp30-Arg40 contributes to quaternary packing. We propose that the charged face comprising of Asp27-Asp30-Glu34-Arg38-Arg40-Glu41-Arg43-Arg44 may be necessary to provide flexibility or stability in the region between the C-terminus and the interdomain/autoinhibitory sequence of RIIalpha, depending on the activation state of PKA. We also discuss the structural requirements necessary for the formation of a stacked (rather than intertwined) dimer, which has consequences for the orientation of the functionally important and distinct faces.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, University of California at Riverside, 92093-0359, USA. dmorikis@engr.ucr.edu