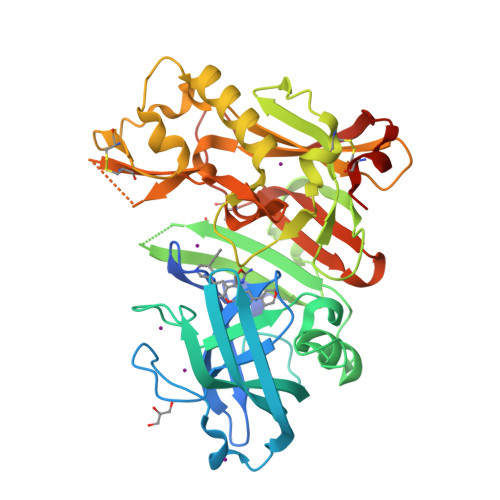
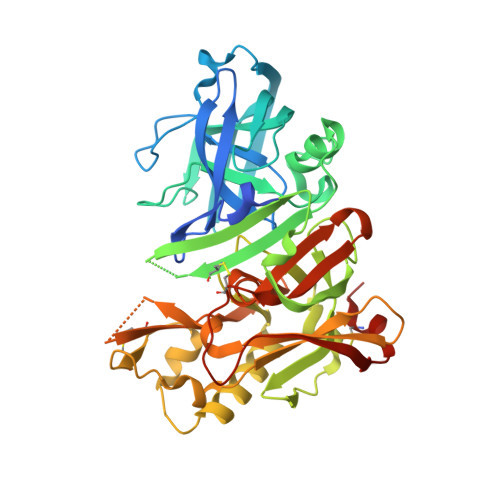
Development of 2-aminooxazoline 3-azaxanthene beta-amyloid cleaving enzyme (BACE) inhibitors with improved selectivity against Cathepsin D.
Low, J.D., Bartberger, M.D., Chen, K., Cheng, Y., Fielden, M.R., Gore, V., Hickman, D., Liu, Q., Allen Sickmier, E., Vargas, H.M., Werner, J., White, R.D., Whittington, D.A., Wood, S., Minatti, A.E.(2017) Medchemcomm 8: 1196-1206
- PubMed: 30108829
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c7md00106a
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5UX4, 5UYU - PubMed Abstract:
As part of an ongoing effort at Amgen to develop a disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer's disease, we have previously used the aminooxazoline xanthene (AOX) scaffold to generate potent and orally efficacious BACE1 inhibitors. While AOX-BACE1 inhibitors demonstrated acceptable cardiovascular safety margins, a retinal pathological finding in rat toxicological studies demanded further investigation. It has been widely postulated that such retinal toxicity might be related to off-target inhibition of Cathepsin D (CatD), a closely related aspartyl protease. We report the development of AOX-BACE1 inhibitors with improved selectivity against CatD by following a structure- and property-based approach. Our efforts culminated in the discovery of a picolinamide-substituted 3-aza-AOX-BACE1 inhibitor absent of retinal effects in an early screening rat toxicology study.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicinal Chemistry , Amgen Inc. , One Amgen Center Drive , Thousand Oaks , CA 91320 , USA . Email: aminatti@amgen.com ; Tel: +1 805 447 4721.