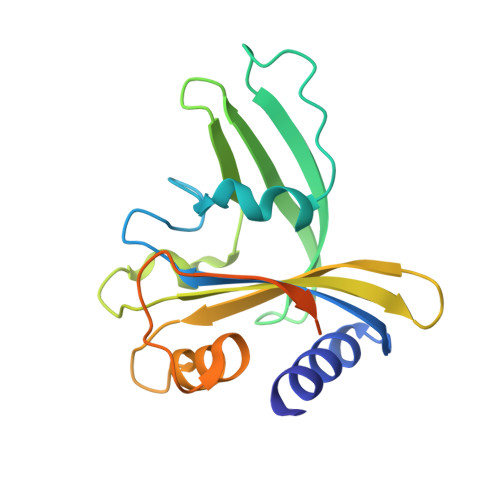
UbaLAI is a monomeric Type IIE restriction enzyme.
Sasnauskas, G., Tamulaitiene, G., Tamulaitis, G., Calyseva, J., Laime, M., Rimseliene, R., Lubys, A., Siksnys, V.(2017) Nucleic Acids Res 45: 9583-9594
- PubMed: 28934493
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx634
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5O63 - PubMed Abstract:
Type II restriction endonucleases (REases) form a large and highly diverse group of enzymes. Even REases specific for a common recognition site often vary in their oligomeric structure, domain organization and DNA cleavage mechanisms. Here we report biochemical and structural characterization of the monomeric restriction endonuclease UbaLAI, specific for the pseudosymmetric DNA sequence 5'-CC/WGG-3' (where W = A/T, and '/' marks the cleavage position). We present a 1.6 Å co-crystal structure of UbaLAI N-terminal domain (UbaLAI-N) and show that it resembles the B3-family domain of EcoRII specific for the 5'-CCWGG-3' sequence. We also find that UbaLAI C-terminal domain (UbaLAI-C) is closely related to the monomeric REase MvaI, another enzyme specific for the 5'-CCWGG-3' sequence. Kinetic studies of UbaLAI revealed that it requires two recognition sites for optimal activity, and, like other type IIE enzymes, uses one copy of a recognition site to stimulate cleavage of a second copy. We propose that during the reaction UbaLAI-N acts as a handle that tethers the monomeric UbaLAI-C domain to the DNA, thereby helping UbaLAI-C to perform two sequential DNA nicking reactions on the second recognition site during a single DNA-binding event. A similar reaction mechanism may be characteristic to other monomeric two-domain REases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biotechnology, Vilnius University, Sauletekio av. 7, LT-10257 Vilnius, Lithuania.