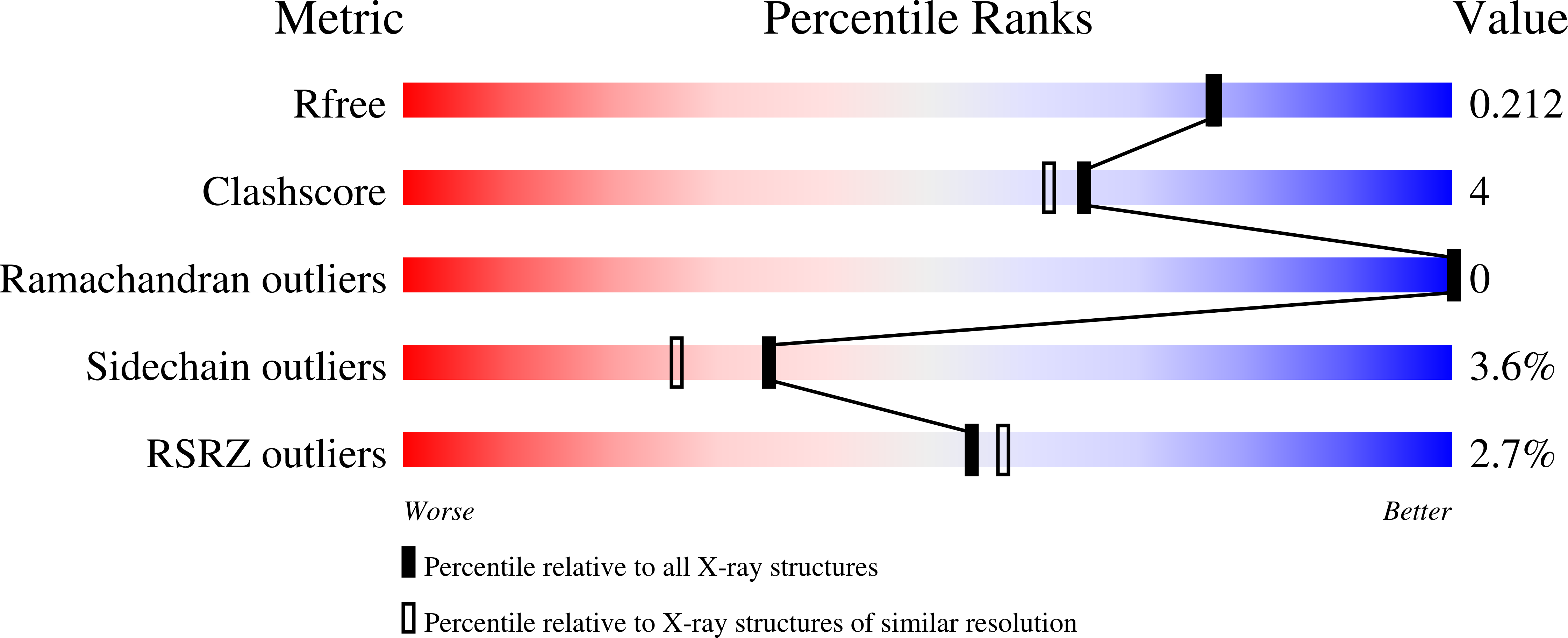
A critical switch in the enzymatic properties of the Cid1 protein deciphered from its product-bound crystal structure.
Munoz-Tello, P., Gabus, C., Thore, S.(2014) Nucleic Acids Res 42: 3372-3380
- PubMed: 24322298
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1278
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NKT, 4NKU - PubMed Abstract:
The addition of uridine nucleotide by the poly(U) polymerase (PUP) enzymes has a demonstrated impact on various classes of RNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs), histone-encoding RNAs and messenger RNAs. Cid1 protein is a member of the PUP family. We solved the crystal structure of Cid1 in complex with non-hydrolyzable UMPNPP and a short dinucleotide compound ApU. These structures revealed new residues involved in substrate/product stabilization. In particular, one of the three catalytic aspartate residues explains the RNA dependence of its PUP activity. Moreover, other residues such as residue N165 or the β-trapdoor are shown to be critical for Cid1 activity. We finally suggest that the length and sequence of Cid1 substrate RNA influence the balance between Cid1's processive and distributive activities. We propose that particular processes regulated by PUPs require the enzymes to switch between the two types of activity as shown for the miRNA biogenesis where PUPs can either promote DICER cleavage via short U-tail or trigger miRNA degradation by adding longer poly(U) tail. The enzymatic properties of these enzymes may be critical for determining their particular function in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, University of Geneva, Geneva, 1211, Switzerland.