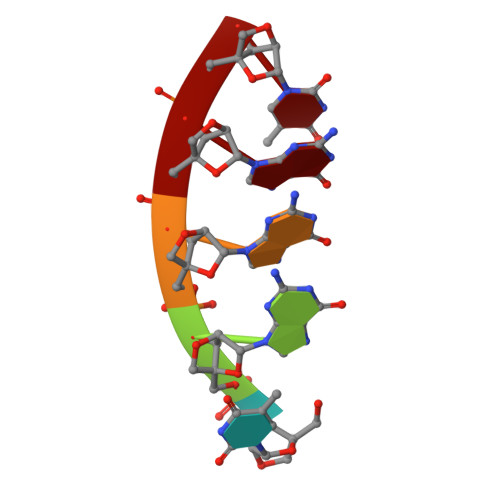
A regular thymine tetrad and a peculiar supramolecular assembly in the first crystal structure of an all-LNA G-quadruplex.
Russo Krauss, I., Parkinson, G.N., Merlino, A., Mattia, C.A., Randazzo, A., Novellino, E., Mazzarella, L., Sica, F.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 362-370
- PubMed: 24531470
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004713028095
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4L0A - PubMed Abstract:
Locked nucleic acids (LNAs) are formed by bicyclic ribonucleotides where the O2' and C4' atoms are linked through a methylene bridge and the sugar is blocked in a 3'-endo conformation. They represent a promising tool for therapeutic and diagnostic applications and are characterized by higher thermal stability and nuclease resistance with respect to their natural counterparts. However, structural descriptions of LNA-containing quadruplexes are rather limited, since few NMR models have been reported in the literature. Here, the first crystallographically derived model of an all-LNA-substituted quadruplex-forming sequence 5'-TGGGT-3' is presented refined at 1.7 Å resolution. This high-resolution crystallographic analysis reveals a regular parallel G-quadruplex arrangement terminating in a well defined thymine tetrad at the 3'-end. The detailed picture of the hydration pattern reveals LNA-specific features in the solvent distribution. Interestingly, two closely packed quadruplexes are present in the asymmetric unit. They face one another with their 3'-ends giving rise to a compact higher-order structure. This new assembly suggests a possible way in which sequential quadruplexes can be disposed in the crowded cell environment. Furthermore, as the formation of ordered structures by molecular self-assembly is an effective strategy to obtain nanostructures, this study could open the way to the design of a new class of LNA-based building blocks for nanotechnology.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemical Sciences, University of Naples `Federico II', Complesso Universitario di Monte Sant'Angelo, Via Cinthia, I-80126 Napoli, Italy.