Targeting of a natural killer cell receptor family by a viral immunoevasin
Berry, R., Ng, N., Saunders, P.M., Vivian, J.P., Lin, J., Deuss, F.A., Corbett, A.J., Forbes, C.A., Widjaja, J.M., Sullivan, L.C., McAlister, A.D., Perugini, M.A., Call, M.J., Scalzo, A.A., Degli-Esposti, M.A., Coudert, J.D., Beddoe, T., Brooks, A.G., Rossjohn, J.(2013) Nat Immunol 14: 699-705
- PubMed: 23666294
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2605
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JO8 - PubMed Abstract:
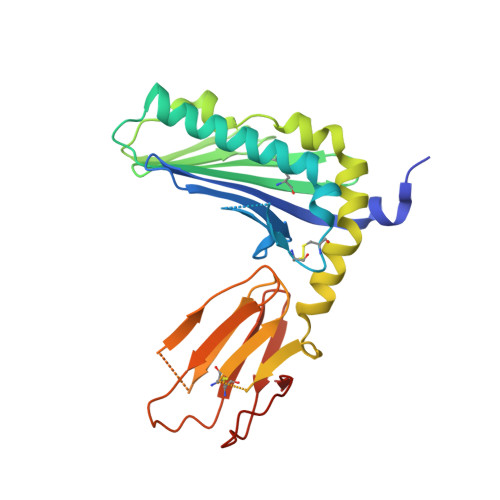
Activating and inhibitory receptors on natural killer (NK) cells have a crucial role in innate immunity, although the basis of the engagement of activating NK cell receptors is unclear. The activating receptor Ly49H confers resistance to infection with murine cytomegalovirus by binding to the 'immunoevasin' m157. We found that m157 bound to the helical stalk of Ly49H, whereby two m157 monomers engaged the Ly49H dimer. The helical stalks of Ly49H lay centrally across the m157 platform, whereas its lectin domain was not required for recognition. Instead, m157 targeted an 'aromatic peg motif' present in stalks of both activating and inhibitory receptors of the Ly49 family, and substitution of this motif abrogated binding. Furthermore, ligation of m157 to Ly49H or Ly49C resulted in intracellular signaling. Accordingly, m157 has evolved to 'tackle the legs' of a family of NK cell receptors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Biomedical Sciences, Monash University, Clayton, Australia.