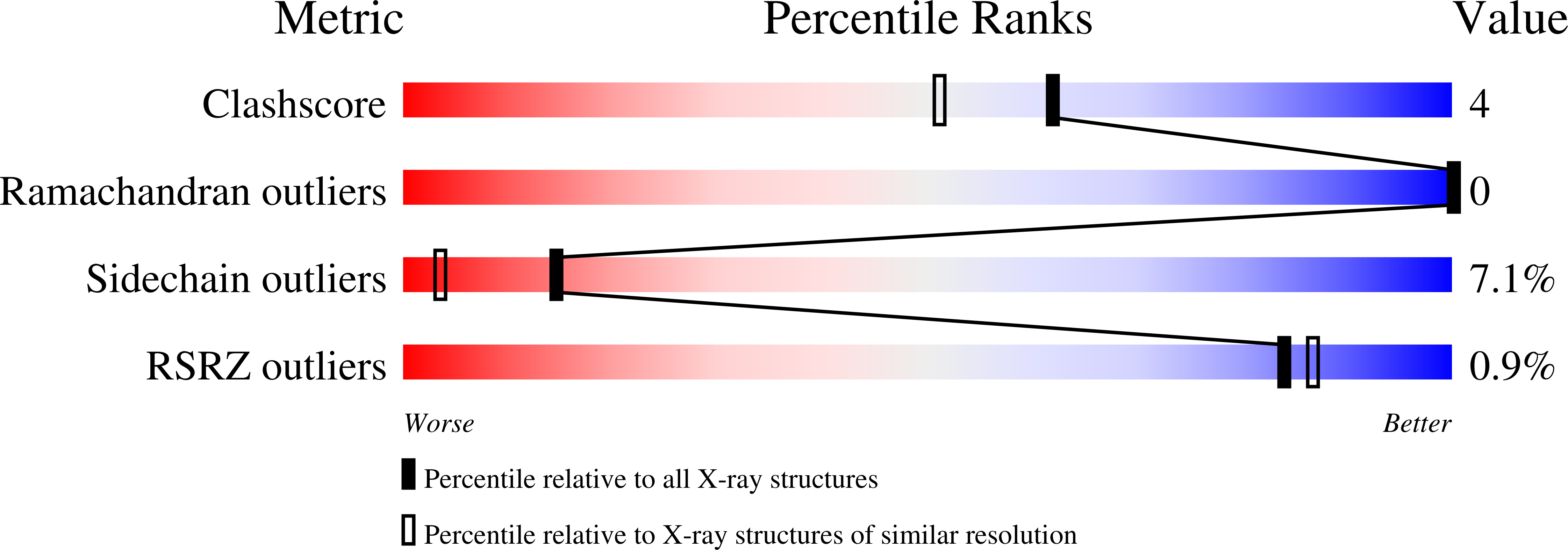
The binding of L-valyl-L-tryptophan to crystalline thermolysin illustrates the mode of interaction of a product of peptide hydrolysis.
Holden, H.M., Matthews, B.W.(1988) J Biol Chem 263: 3256-3260
- PubMed: 3343246
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb3tmn/pdb
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3TMN - PubMed Abstract:
Crystallographic analysis of the binding of mercaptoacetyl-L-valyl-L-tryptophan to thermolysin suggests that this inhibitor is hydrolyzed by the crystalline enzyme. The apparent product of hydrolysis, L-valyl-L-tryptophan (Val-Trp), occupies the S1'-S2' subsites of the active site, not the S1-S1' subsites as observed previously for the dipeptide L-alanyl-L-phenylalanine (Ala-Phe). The difference in binding of Val-Trp and Ala-Phe is consistent with the specificity requirements and preferences of thermolysin. The binding of Val-Trp illustrates the mode of interaction of one of the products of peptide hydrolysis. High resolution crystallographic refinement indicates that the valyl amino group makes three hydrogen bonds to the enzyme and to solvent and, in addition, is 2.8 A from the carboxylate of Glu-143. This is the first instance in which a direct interaction has been observed between Glu-143 and the scissile nitrogen. As such, the study directly supports the mechanism of action for thermolysin proposed by Hangauer et al. (Hangauer, D. G., Monzingo, A. F., and Matthews, B. W. (1984) Biochemistry 23, 5730-5741) and, by analogy, indirectly supports the similar mechanism proposed for carboxypeptidase A (Monzingo, A. F., and Matthews, B. W. (1984) Biochemistry 23, 5724-5729).
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular Biology, University of Oregon, Eugene 97403.