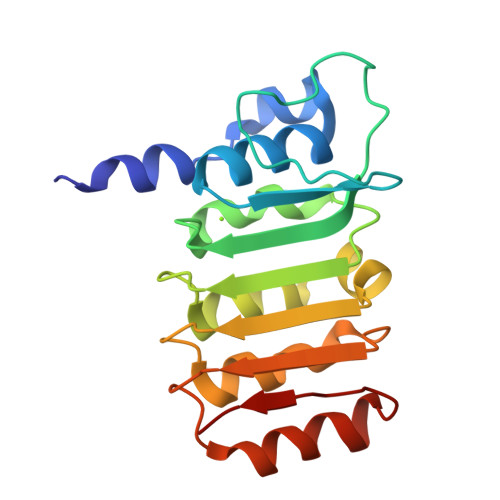
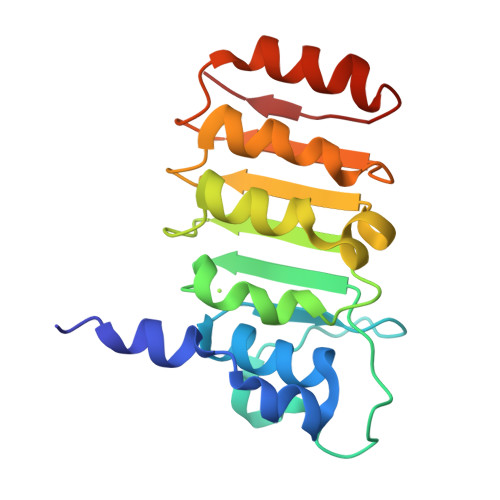
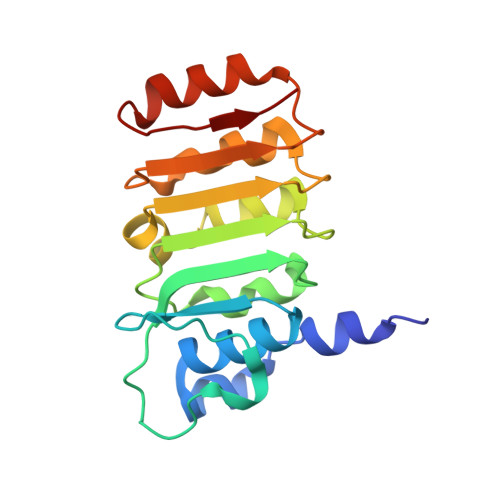
Crystal structure of bovine mitochondrial factor B at 0.96-A resolution.
Lee, J.K., Belogrudov, G.I., Stroud, R.M.(2008) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: 13379-13384
- PubMed: 18768789
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805689105
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DZE, 3E2J, 3E3Z, 3E4G - PubMed Abstract:
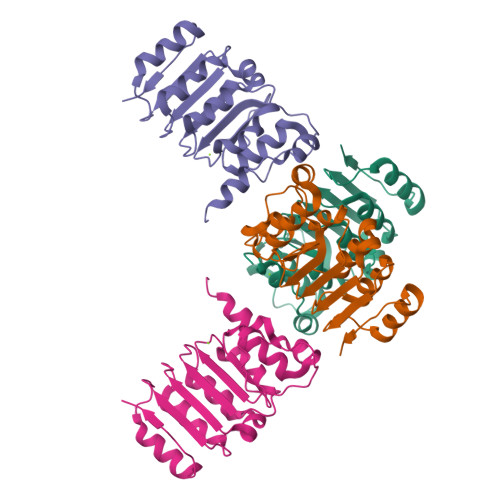
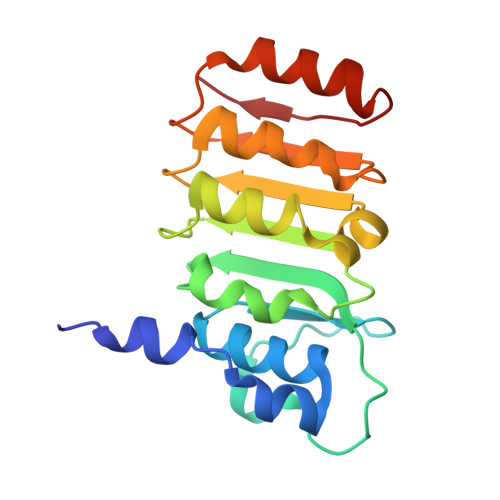
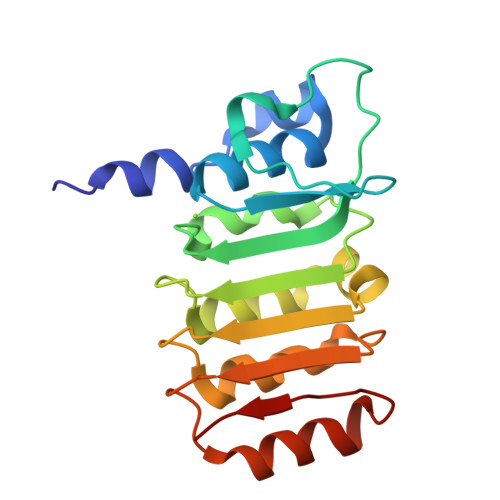
Coupling factor B (FB) is a mitochondrial inner membrane polypeptide that facilitates the energy-driven catalysis of ATP synthesis in animal mitochondria by blocking a proton leak across the membrane. Here, we report the crystal structure of the bovine mitochondrial FB mutant with Gly-3-Glu substitution determined at a resolution of 0.96 A and that of the WT polypeptide at a resolution of 2.9 A. The structure reveals an oblong, oval-shaped molecule with a unique globular N-terminal domain that is proposed to be the membrane anchor domain and the capping region to the C-terminal leucine-rich repeats domain. A short N-terminal alpha-helix, which extends away from the molecule's body, is suggestive of functioning as an anchor for FB to the matrix side of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Identification of a bound Mg(2+) ion reveals that FB is a metalloprotein. We also report the cocrystal structures of FB bound with phenylarsine oxide and Cd(2+), two known inhibitors of the FB coupling activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of California, San Francisco, CA 94158-2517, USA.